Reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as superoxide radicals (O2−), singlet oxygen (1O2), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and hydroxyl radicals (OH−), can accumulate in plant cells under oxidative stresses. ROS can cause damage to lipids, proteins, and DNAs. To cope with this damage, the plant has evolved to be able to produce multiple antioxidant enzymes, which can be indicators for oxidative stresses (Figure 1).
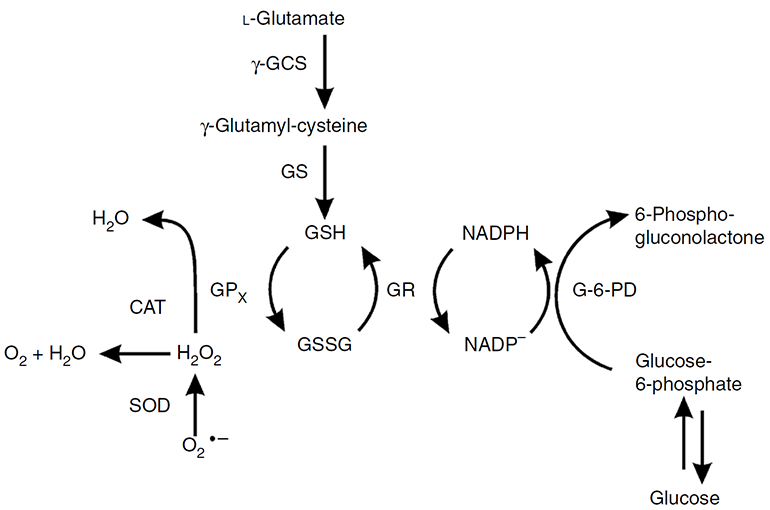 Figure 1. Functions of three antioxidant enzymes--catalase, superoxide dismutase, and peroxidase (represented by glutathione peroxidase (GPx)) (Weydert and Cullen, 2009).
Figure 1. Functions of three antioxidant enzymes--catalase, superoxide dismutase, and peroxidase (represented by glutathione peroxidase (GPx)) (Weydert and Cullen, 2009).
At Lifeasible, we offer a variety of activity analysis for antioxidant enzymes, which include, but not limited to:
Catalase (CAT) activity analysis
CAT catalyzes the decomposition of H2O2 to water and oxygen (O2) (Figure 1). We provide a variety of methods to quantify CAT activity.
(1) Labeling of the unconverted H2O2 with the fluorogenic probe. The product is measured colorimetrically at 570 nm or fluorometrically at Ex/Em = 535/587 nm.
(2) An enzyme-linked colourimetric detection method which employs 3, 5-dichloro-2-hydroxy-benzenesulfonic acid (DHBS), 4-aminoantipyrine (AAP) and peroxidase. The resulting quinoneimine dye is measured at 520 nm.
(3) Reacting with cobalt (II) in the presence of bicarbonate ions. The concentration of end product carbonato-cobaltate (III) complex ([Co (CO3)3] Co) is assessed at 440 nm.
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity analysis
SOD catalyzes the dismutation of superoxide radicals (O2−) to molecular O2 and H2O2 (Figure 2). There are three types of SOD: Cu/Zn SOD (SOD1) in the cytosol, Mn SOD (SOD2) in mitochondria, and EC SOD (SOD3) in extracellular space. We provide various methods for SOD activity analysis.
Peroxidase (POD) activity analysis
POD is a hemoprotein that catalyzes the oxidation of a number of substrates by H2O2: H2O2 +substrate−H2→substrate+2H2O. At Lifeasible, we provide four solutions for POD activity analysis, based on the specific substrates.
Glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activity analysis
The GPx activity analysis is based on the fact that GPx can oxidize the reduced glutathione (GSH) to oxidized glutathione (GSSG) at the presence of H2O2. The generated GSSG is recycled to its reduced state, GSH, by glutathione reductase (GR) and NADPH to generate NADP+ (Figure 1). The GPx activity can be measured based on the decrease of NADPH (absorbance at 340 nm). One unit of GPx activity is defined as 1 mmol of NADPH oxidized per minute at 37 °C. Alternatively, the GPx activity can also be quantified by the fluorescence signal of NADP+ using NADP probe (Ex/Em = 420/480 nm).
Lifeasible, as a specialist in plant physiology, provides state-of-the-art methods for antioxidant enzymes analysis. Our experienced project managers will provide you with professional support to ensure the success of your project. Please feel free to contact with Lifeasible for more information.
Reference
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025