Lifeasible is a plant biotechnology company offering a wide array of molecular breeding services. Our goal is to help plant breeders identify and introduce desirable traits into plant varieties with high efficiency.
GWAS is a method for the study of associations between a genome-wide set of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and desired phenotypic traits. The quantitative evaluation is based on linkage disequilibrium (LD) through genotyping and phenotyping of diverse individuals. Generally, a GWAS infers these associations through a hypothesis test with pertinent test statistics such as Pearson's x2 -test, Fisher's exact test, the F-test, or a regression model under a null hypothesis assumes no association.
As a result of continuously dropping cost for DNA sequencing, whole genome sequencing has been largely available in a wide range of species with phenotype variations, promoting the application of GWAS.
Being a group with diverse knowledge background in genetics, molecular biology, statistics, and bioinformatics, Lifeasible provides worldwide customers with specialized and customized one-stop services in GWAS plant breeding. Our services cover genome sequencing, SNPs discovery, association statistical analysis, as well as validation of candidate gene functions. Our cross-disciplinary experience with a wide range of plant species guarantees superior plant breeding services with a real competitive edges.
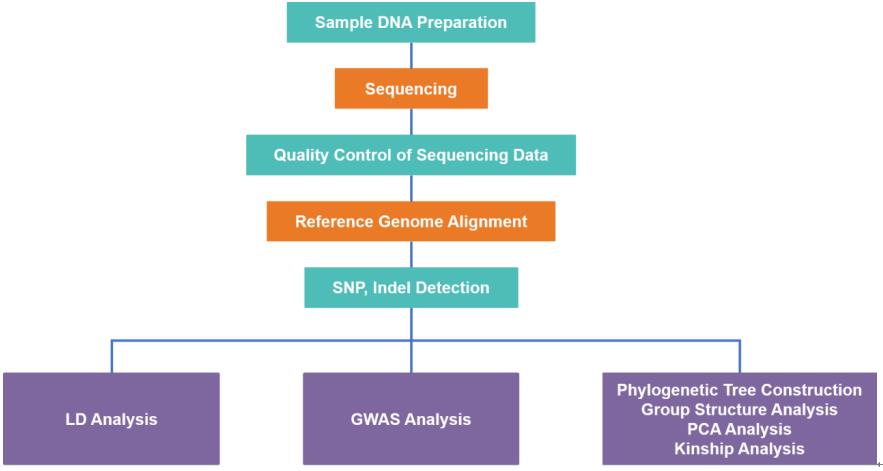
Our services cover SNP detection and annotation, phylogenetic tree construction, linkage disequilibrium analysis, principal component analysis (PCA), group structure analysis, kinship analysis, personalized analysis, etc. In general, three graphs are used for visualization of results:
01
One-stop service from sample processing to data analysis
02
Personalized solutions to meet different requirements
03
Experienced team of scientists and technicians
04
Integrate multidisciplinary expertise
Lifeasible provides a comprehensive technology platform for plant breeding and diversified services to meet the needs of global customers. In addition, we also provide a comprehensive service platform for research on genetically modified plants.
Reference