Lifeasible has established a full-fledged system for thegenetic transformation of Medicago truncatula, a preeminent model for the study of plant growth. Due to its relatively small stature, small diploid genome (450–500 Mbp), short life cycle (about 3 months), and great reproduction ability, M. truncatula has been utilized as an ideal model system for the study of nitrogen fixation, symbiosis, as well as legume genomics. For typical M. truncatula transformation process, a binary vector carrying specific foreign DNA is firstly introduced into Agrobacterium using freeze/thaw method or electric shock method. The transformed Agrobacterium are then cocultivated with explants or seedlingswhich will regenerate to whole plants.
Lifeasible provides multiple innovative variant methods for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of M. truncatula, including:
With a variety of M. truncatula genotypes such as R108-1 and Jemalong A17, multiple Agrobacterium strains including GV3101, AGL-1, EHA105, and C58C1, as well as a wide range of vectors with different selection markers (Kanamycin, Hygromycin, Phosphinothricin, etc.), we are devoted to accommodating the diverse needs of our clients from all over the world.
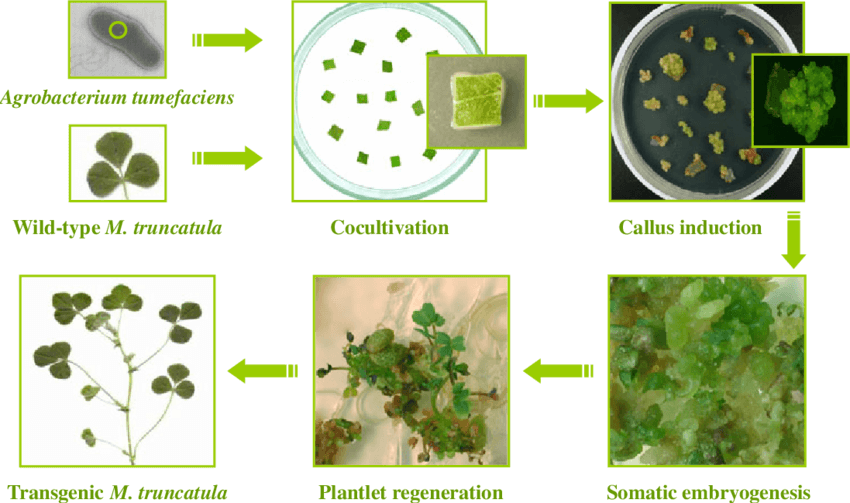 Figure 1. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Medicago truncatula using leaf explants (Peña and Pueyo, 2012)
Figure 1. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Medicago truncatula using leaf explants (Peña and Pueyo, 2012)
Reference: