Populus tomentosa Carr., also known as populus, is a large deciduous tree of the Populus family. It grows fast and has straight trunks, and is widely used in urban and rural greening. Populus tomentosa Carr. has strong adaptability, with well-developed main and lateral roots, dense branches, and leaves. It is a good plant species for fast-growing timber forests, shelter forests, roads, and canals. Populus tomentosa Carr. has straight texture, high fiber content, easy to dry, easy to process, good to paint and has good cementation performance, Populus tomentosa Carr. can be used as materials for construction, furniture, box board, matchsticks, papermaking, etc. It is also the raw material of man-made fibers. In order to further improve the wood properties of Populus tomentosa Carr., speed up the growth time, and optimize the structure of lignin, many genetic modifications have been applied.

Lifeasible provides one-stop services, covering all steps including experimental design, vector construction, plasmid transformation, positive transplant screening and characterization of transgenic Populus tomentosa Carr., our various genetic modification services are as follows:
Gene overexpression is a common technique for studying gene function. The development and utilization of gene overexpression has brought us many conveniences for studying gene function and improving the yield of target products. Through the quantitative overexpression of genes related to linoleic cellulose, lignin, tannin and other chemical components in Populus tomentosa Carr., Thereby increasing the yield of specific compounds. We could help you overexpress many genes including serine hydroxymethyltransferase gene SHMT that affects the process of plant cell carbon metabolism, genes RAP2L15, PtRAP2L14 that affect plant stress resistance, genes PtBBE9a, PtrRHH94 which regulate the growth and development of poplar trees, drought stress gene PtPIP2, salt tolerance related genes GmNHX1, OsNHX1, DREB1A, and many other genes related to important traits of Populus tomentosa Carr.
RNAi technology is a phenomenon of specific gene silencing mediated by double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) and involved specific enzymes. It blocks gene expression at the transcription level and translation level. Through RNAi technology, we can achieve silencing of multiple genes in Populus tomentosa Carr.
Virus induced gene silencing (VIGS) is a genetic technology that inhibits the expression of endogenous genes in plants by inserting recombinant viruses into target gene segments, they can induce plant endogenous gene silencing and cause phenotypic changes, and then study the function of target genes based on phenotypic changes. The VIGS technology is a method of transient transformation and thus can help our customers save time and achieve valuable information for gene functional analysis. With wealth of experience in VIGS, our scientists in Lifeasible can provide our customers with customized protocol for VIGS in Populus tomentosa Carr.
CRISPR gene knockout technology is currently the most widely used gene knockout technology, it provides us with a very powerful and convenient gene editing tool. As a leading company that has been deeply involved in the field of gene editing for many years, through the CRISPR technology, we can knockout Populus tomentosa Carr.’s genes in different ways, including frameshift mutations, multiple deletion of fragments, knockout of non-coding genes, knockout of multiple copies of genes, etc.
The strong scalability of CRISPR system can be used to develop more useful gene editing tools. we have developed many methods that can improve gene knock-in efficiency and achieve precise editing of the Populus tomentosa Carr. genome. For the gene knock-in process, most of CRISPR gene knock-in is done through HDR. However, NHEJ and HDR will occur at the same time due to DSB (DNA double-strand breakage). Therefore, we have developed different methods to increase the probability of HDR, thereby improving the efficiency of gene knock-in.
CRISPR single base editing technology is a hot area of life science research today. As a company that has been cultivating gene editing technology for years, Lifeasible could help our customers achieve the conversion from C to T or A to G in Populus tomentosa Carr. using CBE and ABE, both of which rely on the DNA positioning capabilities of the CRISPR/Cas9 system. During single base editing, the C base deaminase or A base deaminase is located at a specific position in the genome, and it catalyzes the deamination reaction of C or A at a specific position and turns it into U or I. Then it is treated as T or G in the process of DNA replication, realizing the conversion from C to T or A to G.
Sequence-specific control of gene expression on a genome-wide scale is an important approach for understanding gene functions and for engineering genetic regulatory systems, there are many ways to participate in the inhibition of gene expression, one of them is CRISPR Interference (CRISPRi). For the inhibition of Populus tomentosa Carr. genes, we can provide a variety of solutions, including dCas9 binding to targeted DNA and realizing Inhibition of gene transcription through steric hindrance. In addition, gene knockdown can also be achieved by recruiting a fusion protein to the start site of gene transcription.
CRISPRa technology uses the powerful capabilities of Cas9 and sgRNA to fuse or recruit multiple proteins to enhance gene transcription. For Populus tomentosa Carr. genes, we provide VPR technology, SAM technology and Suntag technology to allow the CRISPR system to carry more activation element and achieve a stronger activation effect after synergistic amplification.
The study of gene function has always been the core subject of biological research. The earliest genetic screening system established through forward genetics is very inefficient and has a huge workload. However, the reverse genetic screening system based on CRISPR technology can complete very low-cost mutation library construction work. The gene mutation library construction technology we provide for Populus tomentosa Carr. including gene knockout library construction, gene knockdown library construction, and gene activation library construction. Moreover, single-cell sequencing is available for mutation screening.
DNA-free gene editing technology has received extensive attention from the industry in recent years. We provide DNA free Populus tomentosa Carr. genome editing services, including transient expression of CRISPR/Cas9 plasmid DNA, in vitro transcription of CRISPR/Cas9, and pre-assembled ribonucleic acid composed of purified Cas9 protein and sgRNAs complex. These technologies can avoid the integration of foreign DNA and genome, and reduce off-target effects. In addition, compared with traditional techniques, these techniques can avoid the use of hybridization or backcrossing to isolate CRISPR/Cas9 chimeras, so they are cheaper and have shorter experimental cycles.
Genetic Transformation Process for Populus tomentosa Carr.
So far, the most advanced and widely used method for the development of genetically modified Populus tomentosa Carr. is Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Briefly, the wounded leavesare used as explants and infected by Agrobacterium, and then Adventitious shoots are induced and regenerated into complete plants.
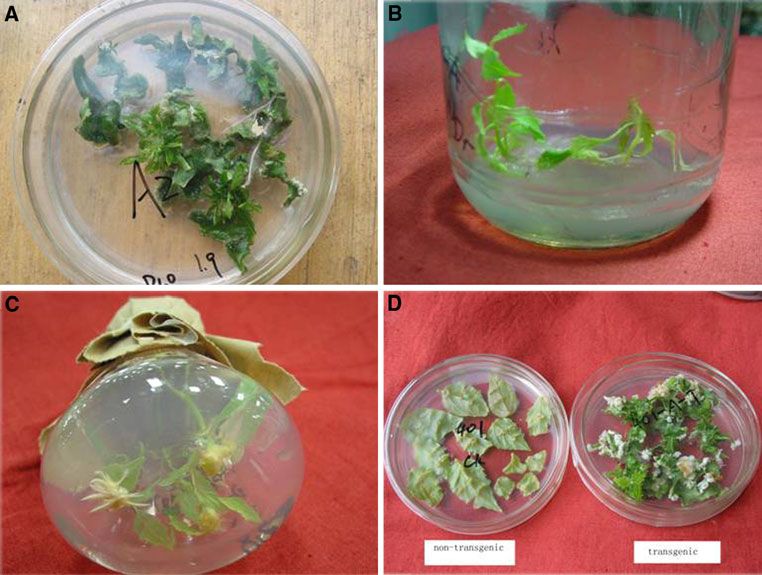 Figure 1. Wounded leaf explants transformation of Populus tomentosa Carr. mediated by Agrobacterium, (a) Adventitious shoot regeneration, (b) Shoots that survived on initial selection medium containing 30 mg/L kanamycin elongated or died on second selection medium with 50 mg/L kanamycin, (c) Rooting of elongated transgenic shoots on half-strength Murashige and Skoog medium, (d) Leaf explants from kanamycin-resistant shoots regenerated adventitious shoots (right), leaves from wild-type control plants wilted or died on the second selection medium (left). (Du N, et al. 2011)
Figure 1. Wounded leaf explants transformation of Populus tomentosa Carr. mediated by Agrobacterium, (a) Adventitious shoot regeneration, (b) Shoots that survived on initial selection medium containing 30 mg/L kanamycin elongated or died on second selection medium with 50 mg/L kanamycin, (c) Rooting of elongated transgenic shoots on half-strength Murashige and Skoog medium, (d) Leaf explants from kanamycin-resistant shoots regenerated adventitious shoots (right), leaves from wild-type control plants wilted or died on the second selection medium (left). (Du N, et al. 2011)
Experts at Lifeasible obtain years of experience to solve technical problems and challenges in Populus tomentosa Carr. transformation. We can draw customized solution to help our customers research on a variety of Populus tomentosa Carr. genes. For more information or any inquiry requirements, please contact Lifeasible. We are more than willing to help our customers with their products.
Reference