Carnivorous plants have five different phyla: Poales (monocots), Caryophyllales (core eudicots), Oxalidales (rosids), Ericales, and Lamiales (asterids). The development of their specialized structures, attractants, and secretions ensures prey attraction and capture. Among carnivorous plants, one of the largest genera and most widely distributed is Utricularia, including terrestrial, epiphytic, and aquatic species. Utricularia gibba is an aquatic plant with sophisticated bladder traps having one of the most complex suction mechanisms for trapping prey. Utricularia gibba becomes an interesting model organism for studying nutrient uptake and complex trap development in rootless plants. However, due to the lack of simple and reproducible gene transfer systems, the mechanisms regulating trap development and the molecular characterization of biophysical processes involved in prey trapping remain largely unknown. Genetic transformation is a fundamental tool for studying the structure and function of plant genes.
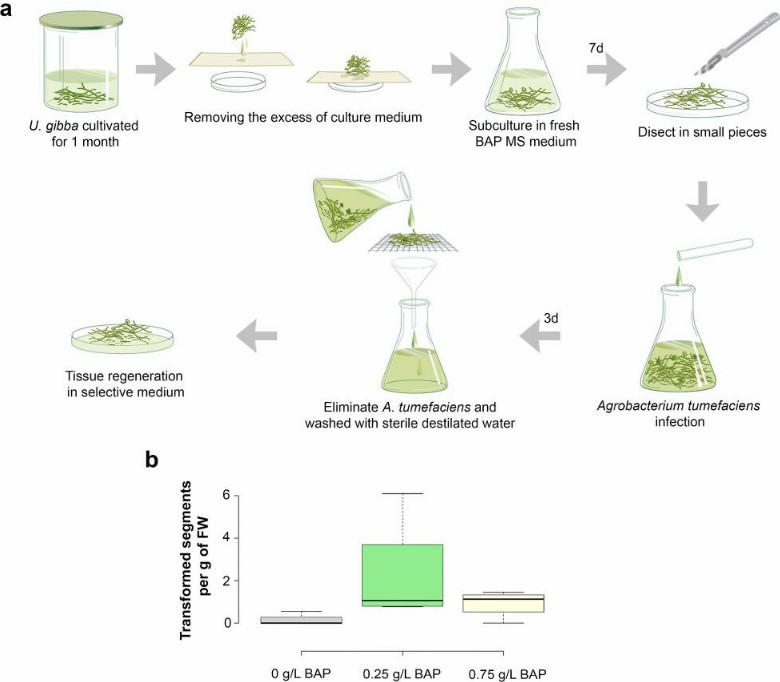 Fig. 1. Protocol and transformation efficiency of Utricularia gibba. (Oropeza-Aburto A, et al, 2020)
Fig. 1. Protocol and transformation efficiency of Utricularia gibba. (Oropeza-Aburto A, et al, 2020)
Lifeasible is an industry leader in plant genetic transformation and is proud to offer cutting-edge genetic transformation services for Utricularia gibba. Our team of biologists and geneticists utilize Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation to establish robust and efficient genetic transformation protocols for Utricularia gibba. This transformation system allows the introduction of exogenous genes into the plant genome, providing valuable insights into the genetic mechanisms underlying trap development and carnivorous plant biology. We can dramatically reduce transformation time to less than 3 months.
Lifeasible offers a simple, fast and reproducible transformation program for Utricularia gibba. We aim to accelerate your research on the complex mechanisms underlying the Utricularia gibba carnivorous lifestyle. If you are interested in our solutions, please contact us for technical consultation and quotation.
Reference:
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025