Lifeasible offers several methods to help determine nitrate and nitrite contents in milk and milk products.
Nitrate and nitrite contents are commonly measured in milk and milk products. Nitrate and nitrite in milk may be obtained from the milk-producing animal's diet, including feeding and water. They are also used as preservatives to inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria. High levels of nitrates and nitrites in milk and milk products can pose a health risk, as they have been linked to an increased risk of bladder, pancreatic, and gastric cancers. They are considered harmful compounds during oxidation and in the degeneration of the digestive system. As a result, it is essential to measure the contents of nitrate and nitrite in milk and milk products to ensure that they are within safe limits and to ensure the safety of the products for consumption.
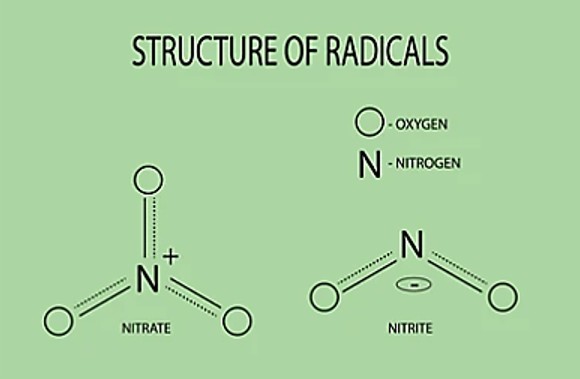 Fig. 1 Structure of radicals of nitrate and nitrite.
Fig. 1 Structure of radicals of nitrate and nitrite.
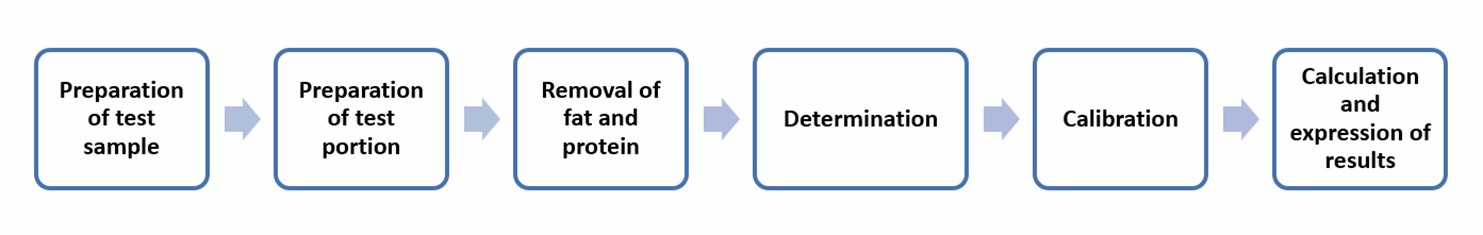
The enzymatic reduction method combined with spectrometry
This method can be used for sample solutions with nitrate concentrations greater than 0.2 mg/L. The method applies to the determination of nitrate and nitrite contents in a wide range of milk and milk products, including kinds of milk (whole, partly skimmed, skimmed, and dried milk), cheeses (hard, semi-hard, soft, processed, and whey cheeses), caseins, caseinates, dried whey, and milk protein concentrates.
The method first precipitates the fat and protein of samples. The nitrate in a portion of the filtrate is then reduced to nitrite by nitrate reductase. Then, sulfonamide and N- (1-naphthyl) ethylenediamine dichloride are added to the unreduced filtrate and the reduced filtrate, respectively. The absorbance is then measured. The nitrate and nitrite contents are obtained by comparing the measured absorbance with those of sodium nitrite calibration solutions.
Main reference standard:
ISO 20541:2008
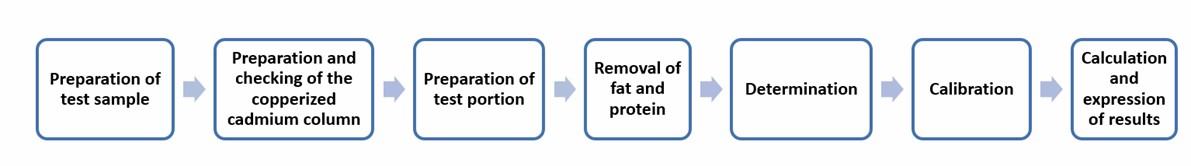
The cadmium reduction method combined with spectrometry
The method applies to milk powders (whole, partially skimmed, and skimmed milk powders), cheeses (hard, semi-hard, soft, processed, and whey cheeses), caseins, caseinates, and dried whey.
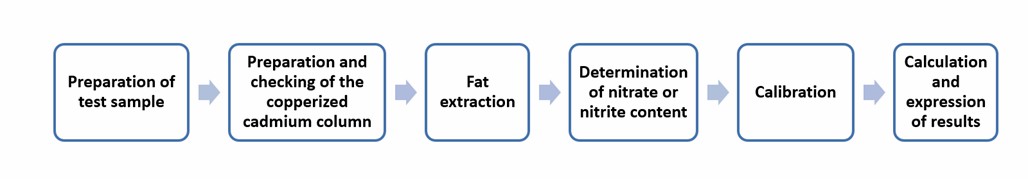
The determination principle of this method is similar to the previous one. The only difference is the use of cadmium to reduce nitrate to nitrite. Therefore, it is necessary to prepare, check, and regenerate the copperized cadmium column.
Operation flow:
Main reference standard:
ISO 14673-1:2004
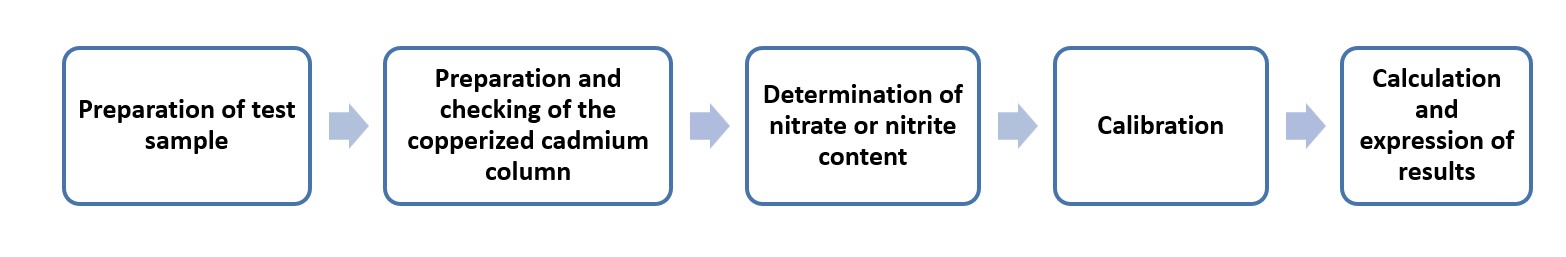
The cadmium reduction method combined with segmented flow analysis
The method can be used to determine the nitrate and nitrite contents of milk, cheese, liquid milk products, dry milk products, and infant foods.
The method is based on dialysis to obtain nitrate and nitrite from the sample, followed by determining the content based on the spectrometric method. Segmented flow analysis is used in this method for rapid analysis and reduction of cadmium contamination in the laboratory. The cadmium is used to reduce nitrate to nitrite.
Operation flow:
Main reference standard:
ISO 14673-2:2004
The cadmium reduction method combined with flow injection analysis
This method is suitable for cheeses (hard, semi-hard, soft, and processed cheeses), whey powder, milk powder, and milk-based infant food. The detection limits of the method are 0.5 mg/kg of nitrate ion and 1.0 mg/kg of nitrite ion, respectively.
In this method, most of the fat in the sample is removed by extraction. A small portion of the de-fatted solution is analyzed by flow injection analysis (FIA). The determination of the content is based on the spectrometric method. The cadmium is used to reduce nitrate to nitrite.
Operation flow:
Main reference standard:
ISO 14673-3:2004
Lifeasible offers services to help determine nitrate and nitrite contents in milk and milk products. Based on that nitrate and nitrite may come from forage, we also help to detect nitrate and nitrite contents in forage. Please contact us to provide you with a combined service.
References
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025