We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve the overall user experience. This includes personalizing content and advertising. Read our Privacy Policy
Lifeasible contributes to the study of key factors in plant-pathogen interactions and offers several services to help study the role of effectors in plant-pathogen interactions.
Pathogens secrete large numbers of effectors (including effector proteins, pathogen secondary metabolites (SMs), and small interfering RNAs (sRNAs)) into the plant to promote infection. They have multiple functions in pathogen-plant interactions. It has been found that effectors can mask pathogens to avoid recognition or attack, resist to plant immunoreactive substances, interfere with host plant physiological activities, manipulate plant immune signaling (Fig. 1), and even regulate host microbiomes. A comprehensive understanding of these effectors and their functions will greatly benefit plant breeding for disease resistance. Lifeasible supports effector research and offers a comprehensive effector research service.
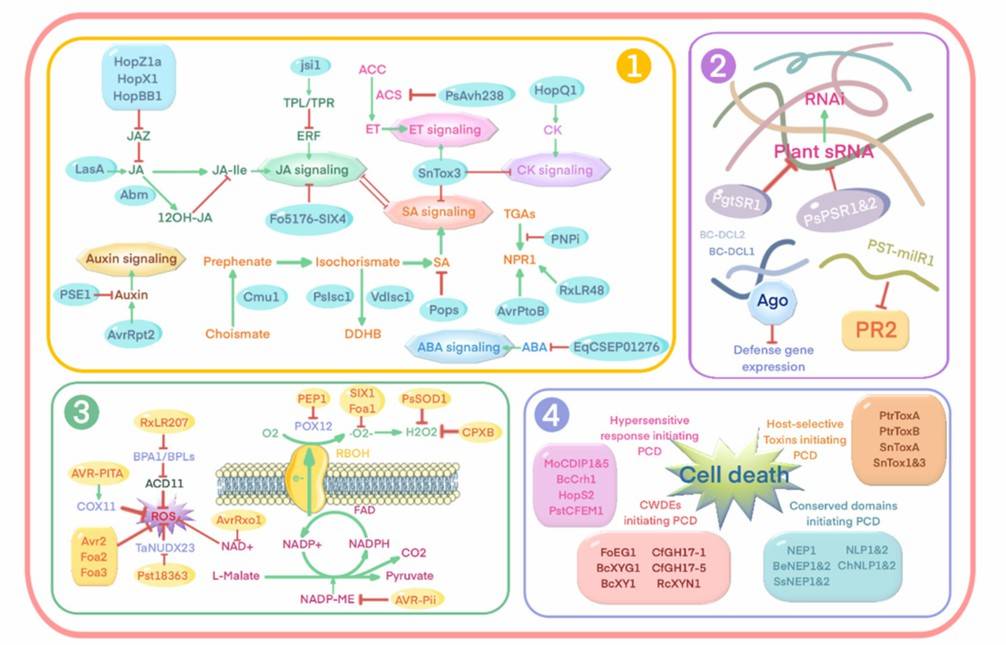 Fig. 1 Effectors manipulate downstream immune responses in host plants (Zhang et al., 2022).
Fig. 1 Effectors manipulate downstream immune responses in host plants (Zhang et al., 2022).
Effector proteins make up the majority of effectors. Our services focus on effector protein research. For other effectors, we offer customized services according to the needs of our clients.
Services for effector proteins
We offer identification and discovery services and functional characterization services for effector proteins. We also offer effector protein interaction studies to help better explore interactions between effector proteins and other proteins.
We help identify and discover effector proteins through three main strategies. We help identify effector proteins based on their secretion properties and structural properties, and we help fully exploit pathogens' genomic information to discover effector proteins.
We help functionally characterize effector proteins. We help with initial functional characterization through knockout or knockdown effector genes or expression effectors by host plants. We help identify effector targets for precise functional characterization of effector proteins. To study the exact function or action mechanism of effector proteins, we offer five major directions, including breaking the physical barrier of plants, creating infestation conditions, masking pathogens, resisting plant immune components, and manipulating plant immune responses.
Services for non-proteinaceous effectors
We also provide research services for non-proteinaceous effectors, including plant SMs and sRNAs. We help discover and validate SMs (such as oxylipins) that enhance pathogen invasion. And we help to determine the structure of these SMs. We help discover and validate sRNAs that regulate pathogen or host gene expression to enhance their virulence. And we help to determine the targets of these sRNAs. The research directions of the exact function or action mechanism of non-proteinaceous effectors are similar to effector proteins.
Experienced
With our extensive experience in protein interactions, secondary metabolite studies, and RNA interference, we can achieve efficient studies of effector proteins, SM effectors, and sRNA effectors.
Customized
The function studies of effectors are broad. We offer customized services based on the needs of our clients or the initial study results.
Avant-garde
We are avant-garde in plant protection, and we are up to date with the latest information on plant immunity, plant protection, and plant-pathogen interactions. We help solve plant protection-related problems with the latest technology.
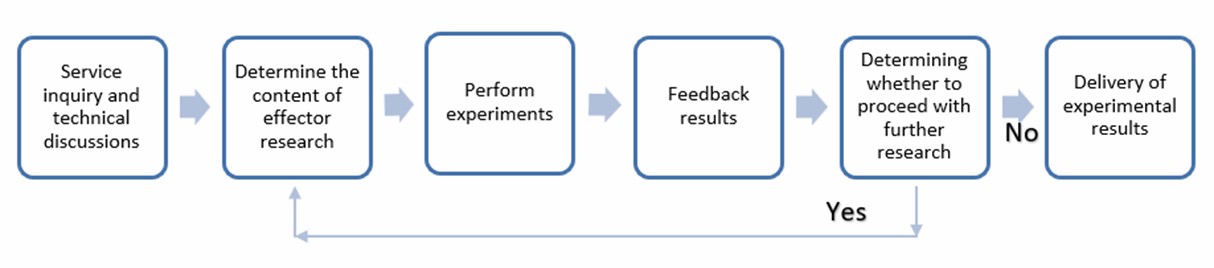
Lifeasible provides professional research services for effector research. We master specialist research techniques. We can help our clients to achieve efficient effector discovery, detection, and function research services. Please contact us to discuss customized research services for effectors.
References
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Mechanisms Regulating Plant Chloroplast Biogenesis
April 15, 2025
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve the overall user experience. This includes personalizing content and advertising. Read our Privacy Policy