The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a dynamic subcellular compartment essential for eukaryotic life because it significantly contributes to the synthesis of basic cellular components, including proteins and lipids, and it serves as an essential structural scaffold to maintain a well-organized spatial distribution of other inner membrane organelles. In addition to proteins such as receptors, ion channels, and enzymes, the ER synthesizes a wide variety of cargo molecules, which control a wide range of physiological and fundamental processes, and are ultimately transported from the ER or retained in this organelle.
Lifeasible, as a leading global company, is committed to helping our customers achieve effective and successful research. We provide functional analysis of plant endoplasmic reticulum, including interference probe, related proteins, and stress-related genes. In addition, we deliver reliable results and reports on time to our customers worldwide.
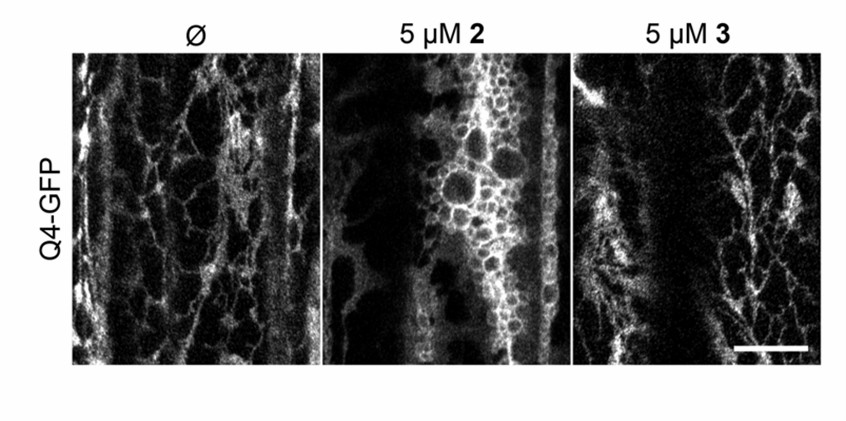 Fig.1 Endoplasmic reticulum structure of Arabidopsis hypocotyl epidermal cells labeled with GFP-Q4. (Dejonghe W., et al., 2021)
Fig.1 Endoplasmic reticulum structure of Arabidopsis hypocotyl epidermal cells labeled with GFP-Q4. (Dejonghe W., et al., 2021)
Lifeasible is always devoted to providing high-quality and satisfactory service to our customers. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Reference
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025