The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a dynamic subcellular compartment that controls secretory pathways at multiple checkpoints in protein biosynthesis, including folding, quality control, signaling, and degradation. In addition, ER plays an important role in abiotic and biotic stress resistance through unfolded protein response signals. The ER is also an essential cellular compartment for calcium storage and carbohydrate metabolism.
Lifeasible is a leading provider of comprehensive, high-quality services for the analysis of plant endoplasmic reticulum proteins. We hope to partner with you to explore new frontiers in plant science and accelerate your discovery.
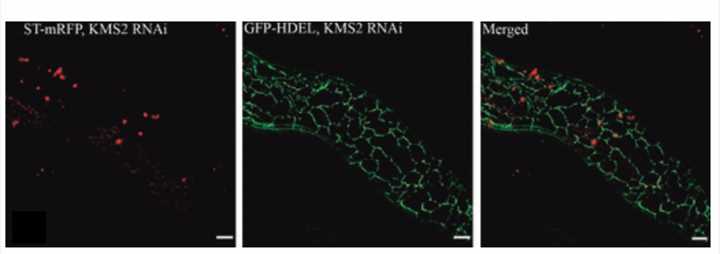 Fig.1. The endoplasmic reticulum network contract as performed of KMS2 RNAi in Arabidopsis hypocotyls. (Wang P, et al., 2011)
Fig.1. The endoplasmic reticulum network contract as performed of KMS2 RNAi in Arabidopsis hypocotyls. (Wang P, et al., 2011)
Lifeasible provides analysis of plant endoplasmic reticulum to our clients worldwide. With years of experience in biological services, our advanced platforms can help our clients solve various difficulties in detecting glutathione with plant research. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Reference
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025