The diameter of KDEL vesicle (KV) is between 200 nm and 500 nm. After budding from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), KV reaches the vacuole directly without passing through the Golgi. In plants, KV formation and vacuolar transport through KV are associated with the KDEL sequence of cysteine protease with KDEL signal. Most soluble ER resident proteins contain the KDEL or HDEL 4 peptide sequence at the C-terminus, called ER resident signal. The Golgi apparatus recognizes this signal and sends the resident proteins that have escaped back to the ER. Besides, the H / KDEL system is highly conserved in plants.
Lifeasible develops an advanced platform equipped with advanced instruments and professional staff for functional analysis of KDEL vesicles with a high standard. We customize featured services according to the customers' demand.
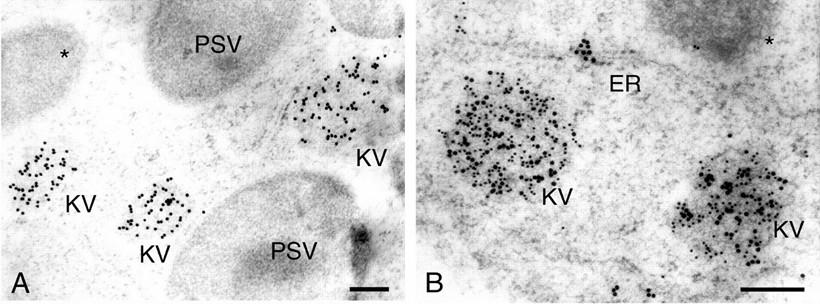 Fig.1. Electron photographs showing that KV is immunogold labeled with antibody to KDEL sequence. (Toyooka K, et al., 2000)
Fig.1. Electron photographs showing that KV is immunogold labeled with antibody to KDEL sequence. (Toyooka K, et al., 2000)
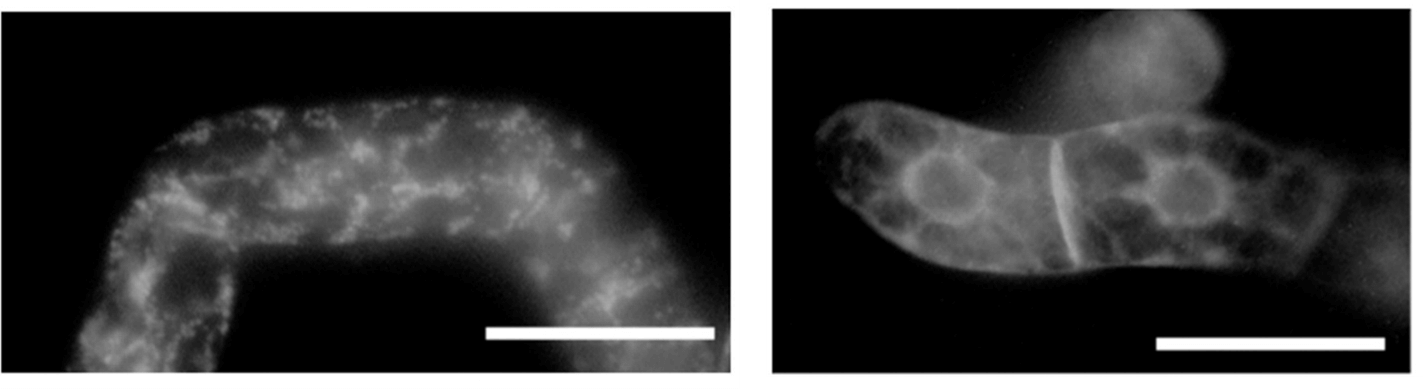 Fig.2. Intracellular localization of SP-GFP-SHEP or SP-GFP-SHEPΔKDEL in tobacco BY-2 cells. (Okamoto T, et al., 2003)
Fig.2. Intracellular localization of SP-GFP-SHEP or SP-GFP-SHEPΔKDEL in tobacco BY-2 cells. (Okamoto T, et al., 2003)
Lifeasible offers services covering functional analysis of the KDEL vesicle to meet your research demands. With years of experience in plant science, our professional platforms can help our clients solve various difficulties. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
References
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025