The ricinosomes (synonymous with precursor protease vesicles) is a novel organelle that sprout from the endoplasmic reticulum of aging tissues. It is also called "Ricinosome" because it is a structure unique to castor seeds. Ricinosomes are round, about 0.9 μm in diameter, with a monolayer membrane structure, and the surface of the membrane is covered with ribosomes. The main component is the Papain cysteine endonuclease (Cys-EP), which can process the glyoxylate malate dehydrogenase precursor protein into mature protein in vitro.
Lifeasible provides functional analysis of the ricinosomes containing storing cys endonuclease and inducing programmed cell death to help our customers worldwide in the field of plant science. Our platform is equipped with cutting-edge facilities and professional experts to support research. Here, we provide various services according to customers' demands.
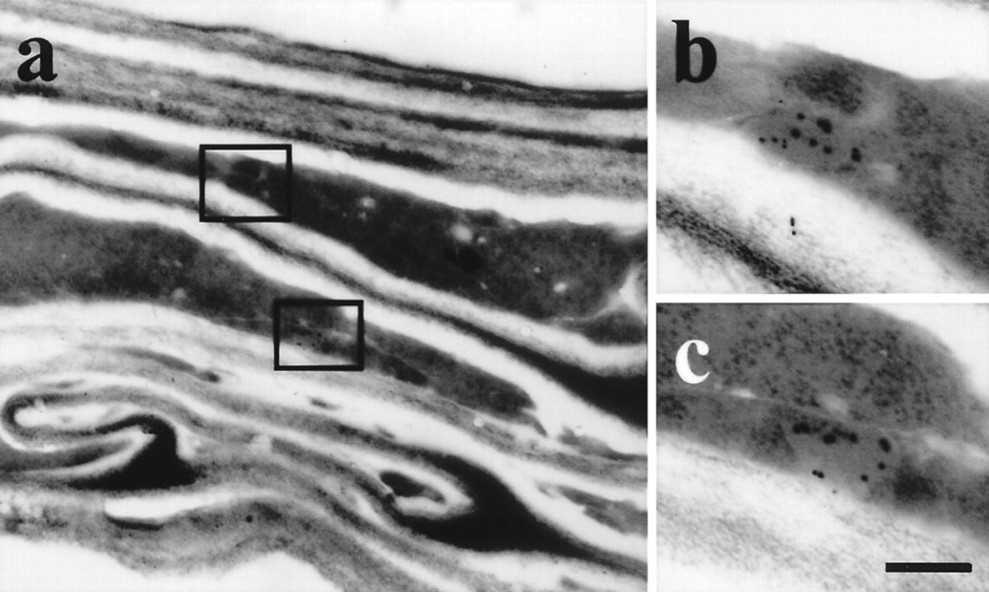 Fig.1. Identification of ricinosomes in developing Ricinus seeds in the collapsed cells by labeling with α-Cys-EP antibody. (Schmid M, et al., 1999)
Fig.1. Identification of ricinosomes in developing Ricinus seeds in the collapsed cells by labeling with α-Cys-EP antibody. (Schmid M, et al., 1999)
Lifeasible has long-term devoted to the development and application of plant science. We are pleased to use our extensive experience and advanced platform to offer satisfied service and qualified products to satisfy each demand from our customers. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Reference
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025