Functional characterization of effector proteins facilitates the development of resistant plants. Lifeasible offers services for the functional characterization of effector proteins.
Pathogen effector proteins perform different functions in plant-pathogen interactions. Many effector proteins have been found to be proteases or plant protease inhibitors (Fig. 1). There are differences in the roles of these two classes of effector proteins in plant-pathogen interactions. Protease-like effector proteins-mediated cleavage can block pattern-triggered immunity (PTI) signaling and manipulate phytohormones. The plant protease inhibitor-like effector proteins mainly function to block plant immune signaling. Determining the specific functions of effector proteins will better assist in and enable breeding for disease resistance in plants. Lifeasible helps to characterize the function of pathogen-effector proteins and contributes to effector protein research of pathogens.
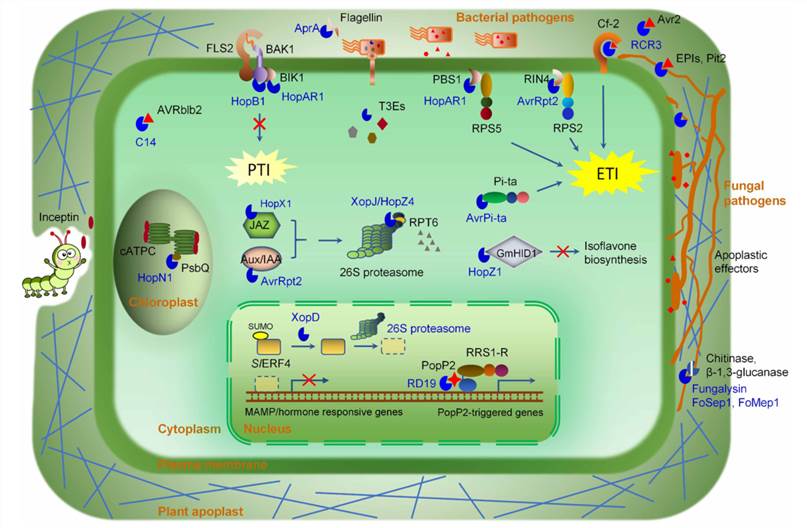 Fig. 1 Schematic of mechanisms of pathogen effectors with protease or protease inhibitor activities (Hou et al., 2018).
Fig. 1 Schematic of mechanisms of pathogen effectors with protease or protease inhibitor activities (Hou et al., 2018).
Lifeasible offers multiple methods to characterize effector proteins. We offer two initial functional characterization services and a precise functional characterization service.
Gene knockouts or knockdowns for initial functional characterization
We often use knockouts or knockdowns to construct effector protein mutants. Our common methods include CRISPR/Cas9 and Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation (ATMT). We help disrupt effector protein-coding genes to obtain mutants. Later, we can use mutant and non-mutant strains to infect the host to help detect the host's infection and immune profiles for initial functional characterization. We can also use host-induced gene silencing (HIGS) or spray-induced gene silencing (SIGS) to disrupt the expression of effector proteins for initial functional characterization.
Plant expression of effector proteins for initial functional characterization
The expression of effector proteins in natural hosts is helpful for the functional characterization of effector proteins. We help realize the expression of candidate effectors in the host plants, and we can realize multiple functional assays to determine the virulence activity of the candidate effectors. For example, we can achieve Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression of candidate effectors and markers in the host plant. For the virulence activity assay of candidate effectors, we can implement host cell death assay, death inhibition assay, and plant growth assay to determine the virulence of candidate effectors.
Investigate action mechanisms and targets of an effector protein
Exact functional characterization requires the investigation of effector targets. We can help explore the targets of effector proteins through plant cell localization studies of effector proteins and protein-protein interaction studies. We help determine the localization of candidate effectors within host tissues to determine the effector protein that can be transferred from the pathogen to the host and to determine where effector targets may be found. Our common approach is adding a GFP tag to the effector protein's N-terminal and then using confocal microscopy to detect effector protein localization. After identifying potential targets based on the effector protein location study, we help design protein-protein interaction experiments to validate the targets of effector proteins and perform precise functional characterization.
Lifeasible specializes in plant protection and has extensive experience studying plant-pathogen interactions. We can customize effector protein overexpression design for different types of host plants. We are familiar with the immune system of plants and can detect several immune profiles of plants for the functional characterization of effector proteins. We specialize in protein-protein interaction studies, which facilitate the precise functional characterization of effector proteins. Please trust us to provide you with the most professional effector protein characterization services and contact us to discuss your project.
References
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025