Forests are the most critical terrestrial ecological plants. Forest systems provide rich biological resources for human beings, harboring many species carrying all kinds of genes and providing species and genetic resources for planted forests. However, forest pests, pathogens, high temperatures, droughts, and other extreme climates are destroying forests. The sharp decrease in forest area is leading to an increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which is one of the causes of global warming, ecological degradation and a severe shortage of wood.
Therefore, to effectively manage existing forest resources and accelerate the process of forest improvement, there is an urgent need for genetic improvement of forest tree resistance and the introduction of genotypes capable of resisting these biological challenges in plantation forests. Conventional tree breeding is an effective way to acquire resistance in forest trees. Still, with the development of biotechnology, genetic engineering techniques are increasingly being applied to the genetic improvement of forest trees.
Lifeasible, a plant biotechnology company representing a high international level, has an experienced research team and a high-end technology platform dedicated to providing customized solutions for genetic improvement of forest tree resistance to customers worldwide.
We usually use biotechnology such as conventional breeding and genetic engineering to improve resistance in forest trees. Conventional breeding generally refers to natural variation selection breeding methods and cross-breeding methods, but only when excellent variation resistance occurs in nature. Genetic engineering is the preferred method in the absence of natural genetic variation for resistance to specific biotic stresses. The main steps in engineering resistance include discovering resistance genes, selecting candidate genes, and transforming and testing.
Through functional genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and epigenomics studies, we obtain genetic information of different tree species, tissues, and organs under different growth conditions, construct high-throughput gene function analysis methods and locate and clone essential functional genes related to resistance and environmental adaptation.
Based on your objectives, and in combination with the species, target resistance, and breeding method, we will compare the screened resistance genes in one step and select the most suitable candidate resistance genes for your study.
We will first recombine the resistance gene, then introduce it into the recipient using Agrobacterium, etc., to obtain a regenerative individual that can express and stably inherit the resistance and test it accordingly.
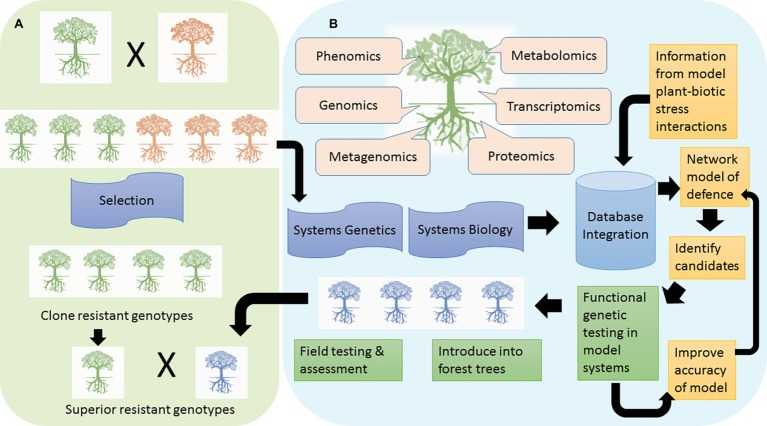 Figure 1. Two avenues to achieving resistance in forest trees are depicted. (Naidoo, S, et al., 2019)
Figure 1. Two avenues to achieving resistance in forest trees are depicted. (Naidoo, S, et al., 2019)
The forest tree resistances we can help our customers improve include insect resistance, herbicide resistance, and stress resistance, as shown below.
The following table shows only a small selection of insect resistance genes, fungal disease resistance genes, virus resistance genes, etc., involved in this service.
| Resistance | Resistance Genes | Transformation |
| Insect resistance | Bt, CvryIc, CpTI, etc. | Agrobacterium |
| Fungi diseases resistance | Chitinase, Ribosome inhibiting protein, RCC2, Ceropin B, Antimicrobial protein, Dihydroflavonol reductase, etc. | Agrobacterium |
| Viruses resistance | TAMV, TMSV-cp, TSMV, BYMV-cp, CMV, PR-1a, etc. | Biolistic technology, Agrobacterium |
| Herbicides resistance | Bar, PAT, EPSP, etc. | Biolistic technology, Agrobacterium |
| Freezing tolerance | hormone synthesis genes, BADH, etc. | Agrobacterium |
Our genetic improvement services for forest tree resistance cover a wide range of species, and information on some of the species we target is shown below.
Main tree species: acacia (Robinia pseudoacacia L.), wood sorrel (Casuarina equisetifolia L.), sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.), camphor pine (Pinus sylvestris var. mongholica Litv.), side cypress (Platycladus orientalis), sea mulberry (Sonneratia caseolaris), etc.
Special species: Stinky cypress (Sabina vulgaris Ant.), tamarisk (Tamarix chinensis Lour.), brome (Caragana), elm (Ulmus pumila L.), date palm (Elaeagnus angustifolia Linn.), ash (Fraxinus chinensis), etc.
Regional tree species: black pine (Pinus thunbergii Parl.), white thorn (Nitraria tangutorum Bobr.), red sand (Reaumuria soongarica), sandy acacia (Sophora moorcroftiana), pokeweed (Haloxylon ammodendron), etc.
Lifeasible is committed to providing professional forest tree resistance genetic improvement services to clients worldwide. We will provide customized services and optimized protocols based on your needs. Please feel free to contact us with questions, inquiries, or collaboration.
Reference