Plant nematodes are one of the main pathogens of crops, which cause significant crop yield reduction and serious economic losses every year. With the wide application of high-throughput sequencing technology, the genomes of many essential plant nematodes have been decoded and reported. Based on this, the origin and evolution of plant nematodes have been further revealed by comparative genomics, and a series of significant advances have been made in functional genomics.
Lifeasible is a credible provider of comprehensive, high-quality services for plant science. We provide an advanced and professional platform for the genomic analysis of plant nematodes according to customer needs. We hope to partner with you to explore new frontiers in plant science and accelerate your discovery.
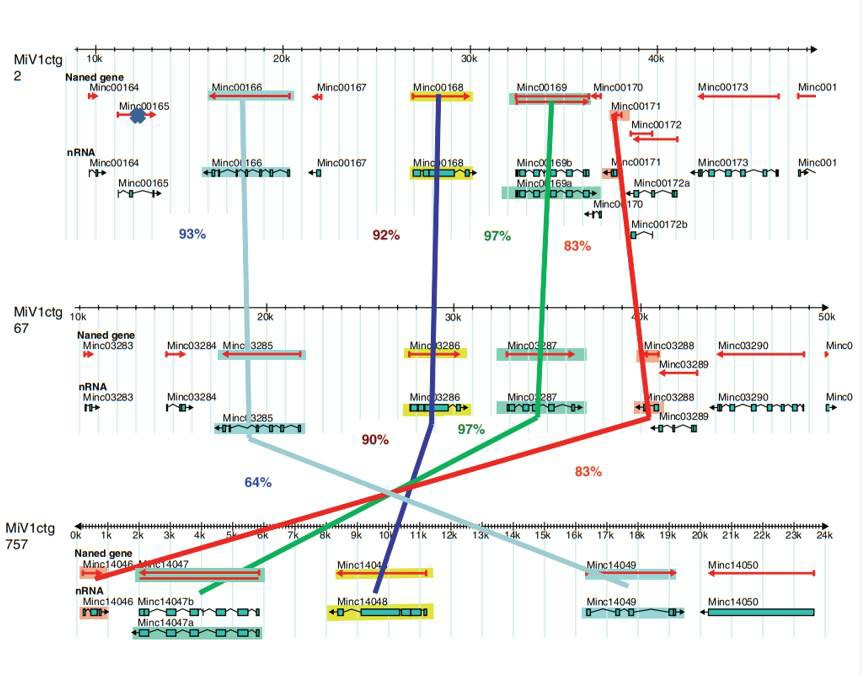 Fig.1 Example of three allelic regions in the M. incognita assembly. (Abad P and McCarter JP, 2011)
Fig.1 Example of three allelic regions in the M. incognita assembly. (Abad P and McCarter JP, 2011)
We provide analysis of the expansion of gene families, mainly including large gene families in plant nematodes, such as G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), G-protein alpha subunits (GPA), SPRY domain protein families, CAZyme, etc.
With years of experience in biological services, our advanced platforms can help our clients solve various difficulties in the research of plant nematodes. Lifeasible provides our clients with direct access to our experts and responses to their questions. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.Reference
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025