Seaweeds are low in lipids. In addition, the chemical properties of seaweed lipids have been the subject of many research, as many are unique and play a key role in nutrition and cell membrane construction. Here, Lifeasible offers professional solutions for the identification of seaweed lipids.
Seaweed is known as a low-energy food. Compared to other species, such as Mangifera indica, seaweeds' lipid content is considered low. In recent years, the lipid composition of seaweeds has attracted considerable interest due to their high content of polyunsaturated fatty acids, particularly alpha-linolenic, octadecatetraenoic, arachidonic, and eicosapentaenoic acids. These acids are considered to be essential nutrients for humans and animals. They play an important role in preventing cardiovascular disease, osteoarthritis, and diabetes, and have antibacterial, antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and antitumour properties. In addition, studies on algal fatty acids (FA) are interesting in terms of their usefulness as potential chemical classification biomarkers. Their lipid profiles can help determine algae's taxonomic position and provide a signature profile for use in organic geochemistry and food studies.
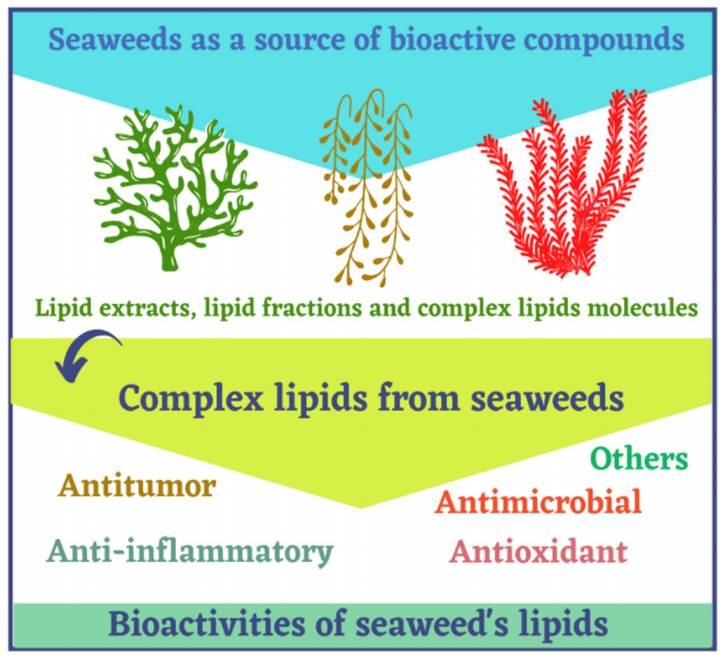 Fig 1. Complex lipids from seaweeds as bioactive compounds with reported bioactivities. (Lopes D, et al., 2021)
Fig 1. Complex lipids from seaweeds as bioactive compounds with reported bioactivities. (Lopes D, et al., 2021)
Lipids in seaweeds are expected to be phytochemicals with intrinsic bioactive properties, with potential applications in pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and cosmeceuticals. However, the complexity and structural diversity of complex lipids has hindered their detailed characterization and development. Our scientists develop modern histological methods and bioinformatics tools for the detailed localisation of the seaweed lipidome from different phyla. Our goal is to identify and characterize complex lipids to analyze the unique features of the seaweed lipidome.
Lifeasible provides a comprehensive service for identifying seaweed lipids to clients worldwide.
Total lipids are extracted from crushed fresh algae (1 kg) using a chloroform/methanol (1:1, v/v) mixture over 2 days at room temperature with stirring for 5 hours. The extracts were filtered using a funnel and washed with distilled water. The lipid content was determined by the weight method and used as a percentage of the dry weight of the algae.
We offer gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry to analyze total fatty acid derivatives, phospholipid fatty acid derivatives, glycolipid fatty acid derivatives, sterols, and neutral lipids.
We offer TLC techniques to analyze the entire sterol and glycolipid composition to visualize the product range.
We offer GC-MS techniques to analyze fatty acid methyl esters, phosphate esters, sterols, and neutral lipids and to differentiate them by identifying their mass spectra.
We offer electrospray ionization ion trap time-of-flight multistage mass spectrometry (LCMS-IT-TOF) combined with high performance liquid chromatography techniques for analyzing active glycolipid fractions to determine molecular formulas.
We evaluate the biological activities of organic extracts (including antibacterial, antiviral, antiprotozoal, antimicroalgal, and antipollution) using in vitro assays and biological effects following oral administration, mainly in animal models.
Lifeasible provides a comprehensive service for identifying seaweed lipids through modern histological methods and bioinformatics tools for the detailed localisation of the seaweed lipidome from different phyla. We are your trusted partner in all aspects of seaweed research. If you are interested in our solutions, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Reference
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025