Maize (Zea mays L.) is a globally important crop and a source of food, animal feed, and industrial raw materials. Maize is also a model system for genetics, evolution, and domestication studies. However, many biotic and abiotic factors affect its productivity, which may lead to low yields in farmers' fields. Genetic improvement through plant breeding utilizing current advances in biotechnology is a feasible and sustainable approach to mitigating the adverse effects of these limitations on production. Genetically modified maize can only be commercialized if it undergoes a thorough safety assessment and is deemed safe. In addition, exogenous genes may cause fragmentation, insertional mutation, activation, or silencing of inherent genes in the maize genome during the integration process of the recipient genome, thereby leading to the formation of new proteins and new metabolites or changes in the levels of existing metabolites, resulting in Unintended effects thus affecting food/feed quality and safety. Therefore, complete molecular characterization of genetically modified maize directly affects the effectiveness of genetically modified safety supervision and is crucial to developers, risk assessors, and regulators of genetically modified maize.
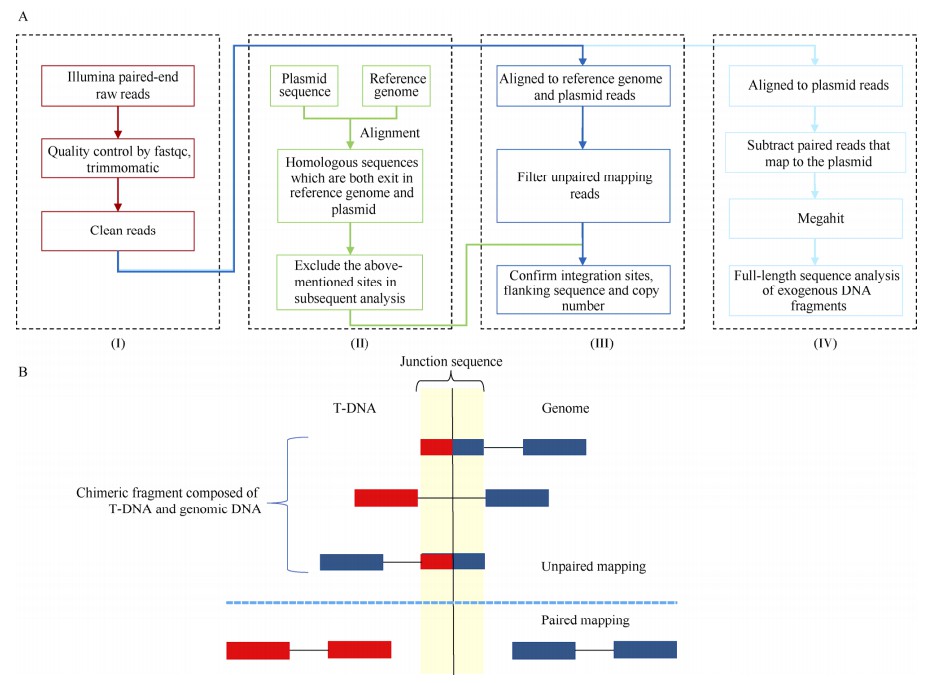 Fig. 1. Pipeline for the molecular characterization of transgenic maize using the WGS method and the schematic diagram of the filtered clean reads. (Yang et al., 2022)
Fig. 1. Pipeline for the molecular characterization of transgenic maize using the WGS method and the schematic diagram of the filtered clean reads. (Yang et al., 2022)

We provide advanced plant genetic engineering services to improve maize genetic traits by applying gene gun, pollen pipeline, Agrobacterium-mediated methods, etc. We can help you cultivate genetically modified maize, such as insect resistance, herbicide resistance, drought resistance, and salt tolerance. With years of experience, Lifeasible provides professional maize molecular characterization analysis services to evaluate the safety of genetically modified maize. We can provide information on the maize molecular characteristics at the chromosome level, including the sequence of the inserted foreign gene, sequence integrity, insertion site, copy number, and flanking sequences.
We have a complete genetically modified maize molecular characterization detection system, including Southern hybridization, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis, PCR-based genome walking, high-throughput sequencing technology, etc. Based on your project requirements, we will choose the best detection method for you to analyze the molecular characterization of genetically modified maize. We can analyze the following genetically modified maize, including but not limited to:
| GM11061 genetically modified maize | Bt genetically modified maize | CryFLIa genetically modified maize | BVLA430101 phytase genetically modified maize |
| GM11019 genetically modified maize | cry2Ab - vip3A - cp4epsps genetically modified maize | BFL4-1 genetically modified maize | ZmWRKY74 genetically modified maize |
| bZIP genetically modified maize | BBHTL8-1 genetically modified maize | GM11048 genetically modified maize | NK603 genetically modified maize |
| MON810 genetically modified maize | BVLA430101 genetically modified maize | - | - |
Work Process of Genetically Modified Maize Molecular Characterization Analysis Based on High-Throughput Sequencing
Advantages of Genetically Modified Maize Molecular Characterization Analysis Based on High-Throughput Sequencing
Lifeasible is committed to providing new technical means for studying molecular characteristics of genetically modified maize, helping you conduct subsequent functional research on genetically modified maize, and evaluating genetically modified maize safety. Please contact us for the best analysis solutions for genetically modified maize molecular characterization.
Reference
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025