Marine invertebrates are the most diverse in the number of species and phyla and account for the majority of marine animals. Marine invertebrates are diverse in size, structure, and function. This diversity of organisms is an excellent material to study and compare various topics. At the same time, the nervous system of marine invertebrates is relatively simple, which is a good choice for neuroscience research.
With the complete sequencing of the genomes of some marine invertebrates, such as Apostichopus japonicus, Ascidian, Crassostrea gigas, and Brachionus koreanus, the study of these species has entered the post-genomic era. The application of epigenetic sequencing technology CHIP-seq on these marine invertebrates has deepened the understanding of marine invertebrates.
As a professional animal sequencing company, Lifeasible can provide efficient and accurate marine invertebrate ChIP-seq solutions. We help our customers to build regulatory networks of target genes, perform genome-wide characterization of histones, and determine candidate genes and vital regulatory mechanisms related to target traits to help them achieve a series of research results in the genetic breeding and developmental evolution of marine invertebrates.

Our service first enriches target protein-binding DNA fragments specifically by ChIP then purifies and constructs libraries; the enriched DNA fragments are then subjected to high-throughput sequencing. The millions of sequence tags are precisely positioned on the genome to obtain genome-wide information on DNA segments that interact with histones, transcription factors, etc.
Heat stress is a significant risk to the survival of the marine invertebrate Apostichopus japonicus. We performed genome-wide characterization of H3K9ac using ChIP-seq at room temperature and under heat stress conditions. The results showed that H3K9ac is an epigenetic regulator of multiple transcription factors in heat stress. We identified five genes that up-regulate H3K9ac modifications and two genes that down-regulate H3K9ac modifications.
We analyzed genes regulated by HSF1 in response to heat stress in Crassostrea gigas by ChIP-seq. The results show that one small HSP gene, four HSP70 genes, and two HSP40 genes bind to HSF1 to counteract heat stress. ChIP-seq can further help our clients to explore the regulatory network of heat tolerance mechanisms in marine invertebrates.
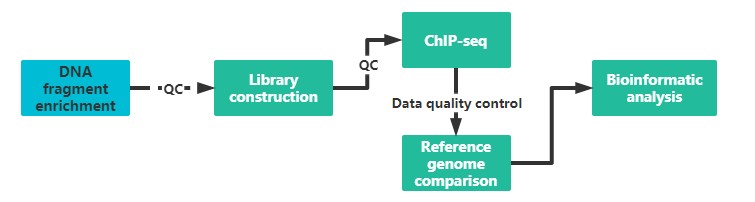
It is recommended to provide two sample preparations, if possible, to ensure the quality and continuity of the experiment.
Lifeasible can provide customized marine invertebrate ChIP-seq services to help build regulatory networks that control the development of these simple chordates and provide research information for more complex organisms. Please feel free to contact us with questions, inquiries, or collaborations.
References
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025