Soil contains the most diverse microbial communities on earth, such as bacteria, archaea, fungi, viruses, protists, and some microfauna, which can be collectively referred to as the soil microbiome.
Soil microbial metabolomics is a research area of soil microbiomics, and its research breadth and complexity far exceed that of a single flora because of the extremely complex soil environment, the diversity of its microbial communities, and the life activities of various microorganisms that create a huge system of metabolites.
Lifeasible can qualitatively and quantitatively analyze the microbial metabolites (including all low molecular weight metabolites) in soil samples with the help of high-throughput technological tools and based on appropriate improvements to obtain reliable information on soil microbial metabolism.
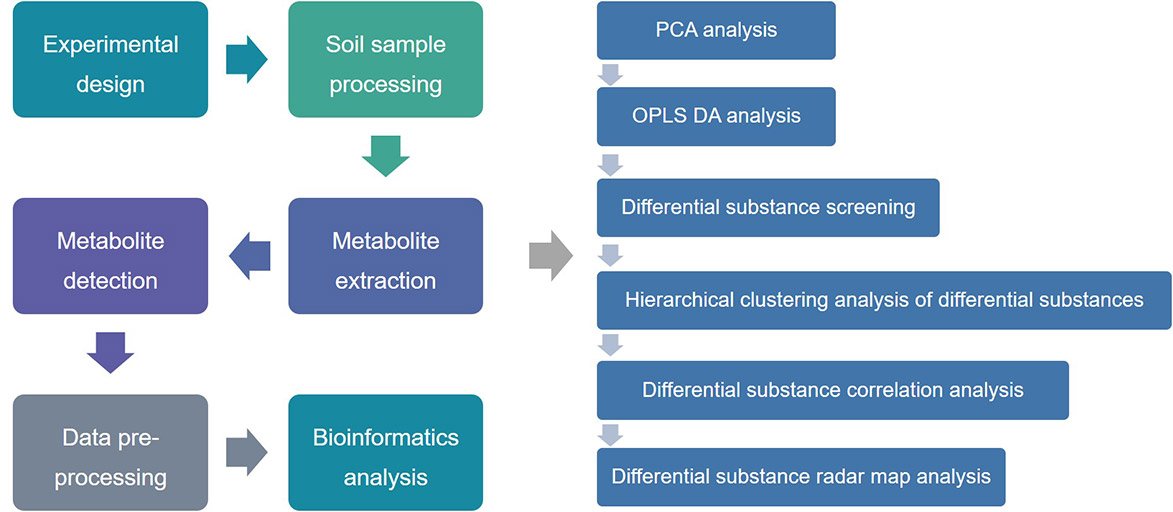 Figure 1. The basic analytical procedure of soil microbial metabolomics.
Figure 1. The basic analytical procedure of soil microbial metabolomics.
The extraction of metabolites is the key to the metabolomic analysis of soil microorganisms, and Lifeasible currently performs extraction of soil metabolites by salt solution, chloroform fumigation, and organic solvents.
Lifeasible uses precise, sensitive, high-throughput analytical methods and technology platforms to comprehensively analyze all small molecule metabolites in soil systems, reflecting the full spectrum of metabolite information.
The main analytical techniques we use include NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance), LC-MS (liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry ), GC-MS (gas chromatography-mass spectrometry), CE-MS (capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry), LC-ESI-MS-MS (liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectroscopy), CE-RP-UPLC (capillary electrophoresis reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography), HILIC/UPLC-TOF-MS (hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography/ultra-performance liquid chromatography-time-of-flight -mass spectrometry), HPLC-MS (high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry), UPLC-MS (ultraperformance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry), and multidimensional chromatography.
We provide untargeted and targeted analysis for hundreds of metabolites containing primary metabolites such as amino acids, sugars, alcohols, organic acids, fatty acids, and secondary metabolites such as terpenoids and polyketides.
Since the data obtained from metabolomics are very complex and correlated, it is not possible to analyze all data in detail and independently, so Lifeasible uses multivariate analysis and pattern recognition techniques to further analyze the pre-processed data. We use PCA (principal component analysis), PLS-DA (partial least squares discriminant analysis), orthogonal algorithms, artificial neural networks, and evolutionary-based computational algorithms, NLM (nonlinear mapping), K-NN (k-nearest neighbor method), and OPLS-DA (orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis), HCM (hierarchical clustering method), and NMF (non-negative matrix factorization) pattern recognition techniques are used for their data analysis. SIMCA-P, SPSS, SAS, XCMS, and MestReNova are the software we commonly use in data analysis.
Lifeasible has extensive experience in sample pre-treatment to fully extract metabolites from the soil, and our platform has a wide range of assays to detect multiple types of metabolites in soil. To learn more about how we can serve you, feel free to contact our staff for the latest information.