Nanotechnology has broad application prospects in plant protection. Lifeasible is dedicated to helping research the application of nanotechnology in plant protection, and we provide research services on nanotechnology in plant disease control.
Nanotechnology, the sixth revolutionary technology, has been widely evaluated for its utility in plant disease control. Many nanoparticles have been found to have better anti-microbial functions. For example, silver nanoparticles have antifungal activity against Fusarium moniliforme, Penicillium brevicompactum, and Helminthosporium oryzae. Nanomaterials can provide a wider specific surface area, and applying anti-microbial and anti-pest agents in nano form can enhance their anti-microbial and anti-pest activities. This also helps to reduce the use of agrochemicals, thus reducing the problem of agrochemical residues. In addition, nanomaterials also play a role in the control of plant viruses. For example, engineered nanomaterials composed of two metal-based nanoparticles (NP Fe2O3 or TiO2) significantly inhibited the proliferation of tobacco (Nicotiana benthamiana) and turnip mosaic virus (TuMV). The role of some nanoparticles in plant disease control is illustrated in Fig. 1.
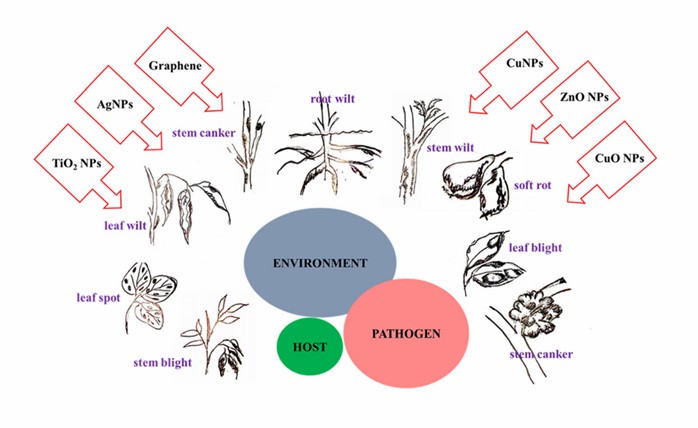 Fig. 1 Schematic showing the disease triangle, common disease symptoms in plants, and examples of nanoweapons (antimicrobial nanomaterials) to achieve disease control (Rajwade et al., 2020).
Fig. 1 Schematic showing the disease triangle, common disease symptoms in plants, and examples of nanoweapons (antimicrobial nanomaterials) to achieve disease control (Rajwade et al., 2020).
Lifeasible provides services to help various studies on nanotechnology in plant disease control.
Preparation of nanomaterials
The size and shape of nanoparticles determine the properties and applications of nanomaterials. The size and shape of nanoparticles need to be better controlled in preparing nanomaterials. We can prepare nanomaterials, including inorganic nanomaterials, organic nanomaterials, and organic-inorganic hybrid nanomaterials, by a variety of physical, biological, and chemical methods using specialized equipment. We have accumulated extensive experience in nanoparticle size and shape control. We can help manufacture nanomaterials with certain nanoparticle sizes and shape control to facilitate our customers' research on the role of nanomaterials in plant disease control.
Research on the mechanism of plant disease control by nanomaterials
We provide services to study the mechanisms of nanomaterials in plant disease control, including anti-microbial, anti-viral, anti-pest, plant immune stimulation, and weed control mechanisms. We will initially determine the general disease mechanisms and then help our clients to explore more in-depth disease control mechanisms. The general plant protection mechanisms we determined include direct contact damage, photocatalytic generation of reactive oxygen species, promoting the release of toxic ions, blocking electron transport, and provoking plant resistance.
Optimization of nanomaterials for plant disease control
We provide nanomaterial optimization services to enhance the role of nanomaterials in plant disease control. We optimize nanomaterials from three aspects: the size of nanoparticles in nanomaterials, the shape of nanomaterials, and the composition ratio of nanomaterials. We perform targeted optimization with reference to the properties of other nanomaterials used for plant disease control.
Lifeasible helps research nanotechnology in plant disease control and provides nanomaterials preparation, plant disease control mechanism study of nanomaterials, and nanomaterials optimization services for convenient nanomaterial study in plant disease control. If you need the above services, please contact us.
References
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Mechanisms Regulating Plant Chloroplast Biogenesis
April 15, 2025