There are nearly 1 billion patients with brain diseases worldwide, yet the vast majority of brain diseases have no effective treatment. Therefore, research on the mechanisms of brain diseases and developing new drugs are very urgent. Due to evolutionary similarity, the non-human primate brain is highly like humans in many aspects, such as structure and functional activities. Compared with other model animals, non-human primates have significant advantages in studying human diseases, especially cognitive and neurological diseases.
Epigenetic regulatory mechanisms largely influence the transcription of genes. Chromatin accessibility is highly specific between cell types, developmental time points, and pathological conditions. Therefore, determining chromatin accessibility at specific developmental stages and in specific cell types and its relationship to transcriptional changes is important for the understanding of brain diseases.
Lifeasible has been deeply involved in animal sequencing for many years and is committed to providing innovative, flexible, and customizable non-human primate ATAC-seq solutions to clients worldwide. Our epigenomic sequencing services support our clients' research into higher functions of human perception, cognition, and behavior, as well as help study brain disease mechanisms and therapeutic approaches.

We examined the chromatin accessibility of human, chimpanzee, gorilla, orangutan, and macaque lymphoblastoid cell lines using ATAC-seq technology to analyze transcription factor (TF) and regulatory element (RE) binding sites. And the chromatin states of RE were classified according to a hierarchy of functionally interpretable epigenetic states. Combined with ChIP-seq and RNA-seq, this work shows that the evolution of gene regulation is strongly influenced by the coordination of epigenetic activities in gene regulatory structures.
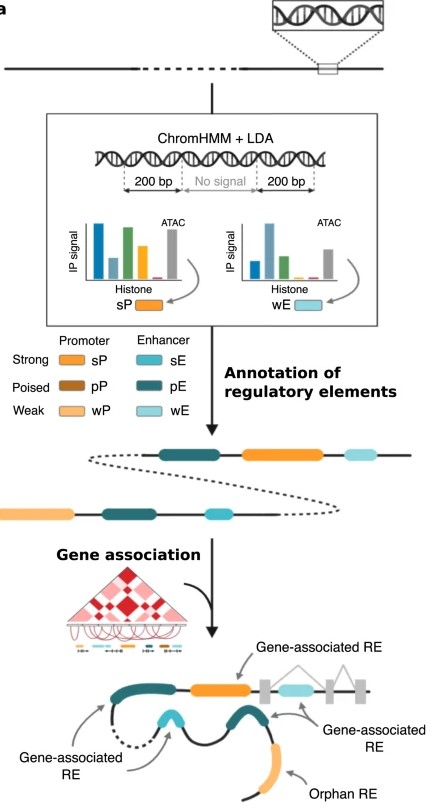 Figure 1. Annotate and classify RE based on a combination of chromatin marks and ATAC-seq signals. (García-Pérez, R, et al. 2021)
Figure 1. Annotate and classify RE based on a combination of chromatin marks and ATAC-seq signals. (García-Pérez, R, et al. 2021)
The rhesus monkey is a major model animal in neuroscience. To gain insight into the brain, we used ATAC-seq to investigate open chromatin regions in the hippocampal CA1 of eight rhesus monkey brains and several cortical regions of the rhesus monkey brain, revealing profiles of CA1 and cortical-specific open chromatin regions.
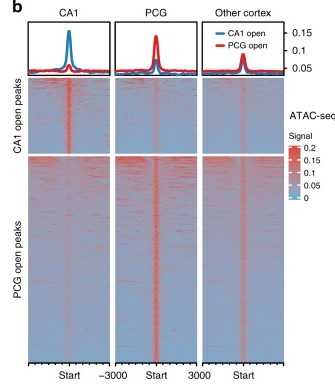 Figure 2. ATAC-seq signaling in rhesus monkey CA1, PCG, and other cortical regions. (Yin, S, et al. 2020)
Figure 2. ATAC-seq signaling in rhesus monkey CA1, PCG, and other cortical regions. (Yin, S, et al. 2020)
Huntington's Disease (HD) is a fatal neurodegenerative disease. To investigate the altered epigenetic profile of HD disease, we examined the global transcriptional and chromatin accessibility dynamics during astrocyte differentiation in vitro in a transgenic rhesus monkey model of HD using ATAC-seq technology. The results showed that THSSs (Tn5 hypersensitive sites) enrichment and transcription factors (TFs) occupancy were extensively altered, and E2F was dysregulated during in vitro HD astrocyte differentiation.
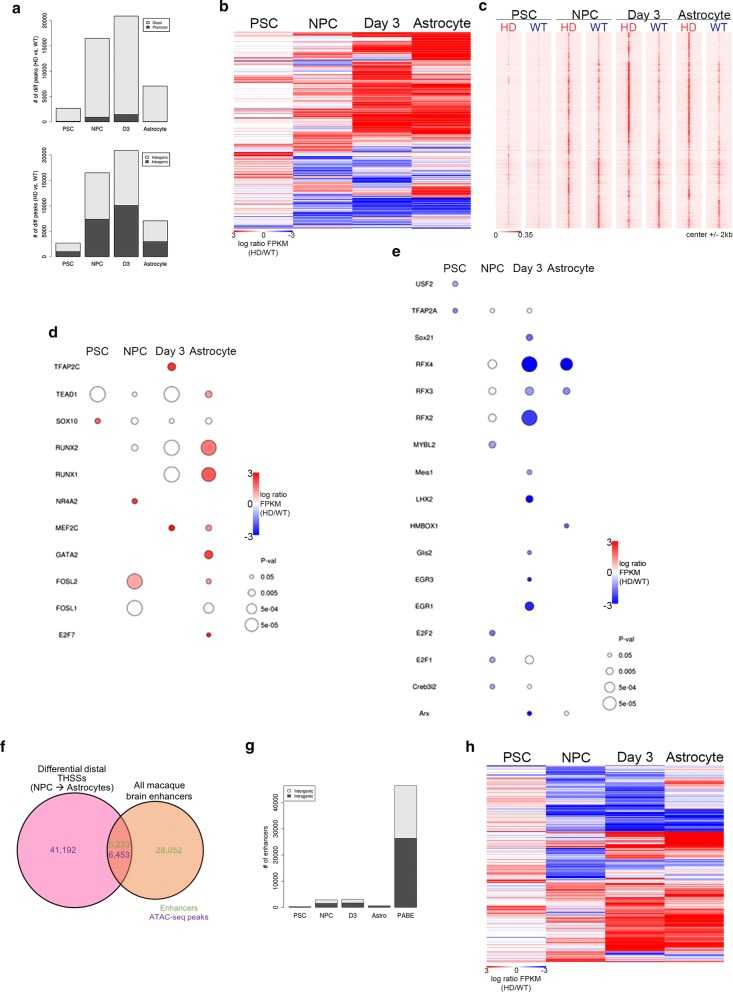 Figure 3. Characterization of differential distal THSSs during HD astrocyte differentiation. (Goodnight, A. V, et al. 2021)
Figure 3. Characterization of differential distal THSSs during HD astrocyte differentiation. (Goodnight, A. V, et al. 2021)
Please note: Ensure sufficient dry ice when transporting samples to avoid temperature rise to destroy cell activity.
Lifeasible's animal-oriented sequencing technology platform can provide our clients with non-human primate ATAC-seq services to meet all their needs. Our extensive project experience, scientific protocol design, and professional analysis team ensure that every step of the process is completed with excellence. Please feel free to contact us for questions, inquiries, or collaboration.
References
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025