The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a membrane that performs many essential functions in a eukaryotic cell. It forms a 3-D lace-like network consisting of continuous tubules and flat lamellae, whose motility can be observed in living cells as ER structures in tubular flow cytoplasmic chains or tubular structures and lamellar plates. These changes include the movement of the tubules as well as their growth and contraction.
Lifeasible provides observation services of endoplasmic reticulum in plants to help our customers worldwide in plant scientific research. Our platform is equipped with cutting-edge facilities and professional experts to support research. Here, we provide various services according to customers' demands.
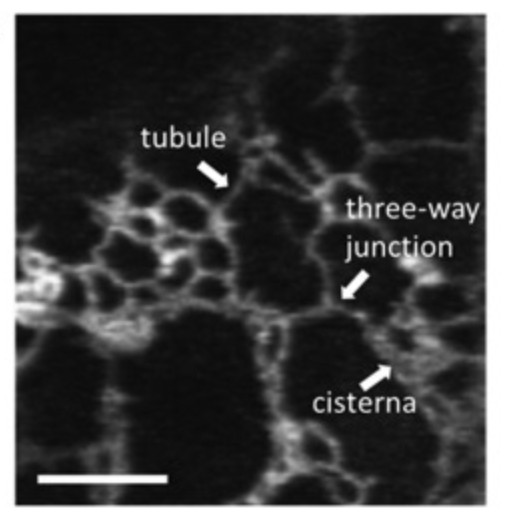 Fig.1 Confocal microscopic image of the cortical ER region of tobacco leaf epidermal cells. (Brandizzi F., 2021)
Fig.1 Confocal microscopic image of the cortical ER region of tobacco leaf epidermal cells. (Brandizzi F., 2021)
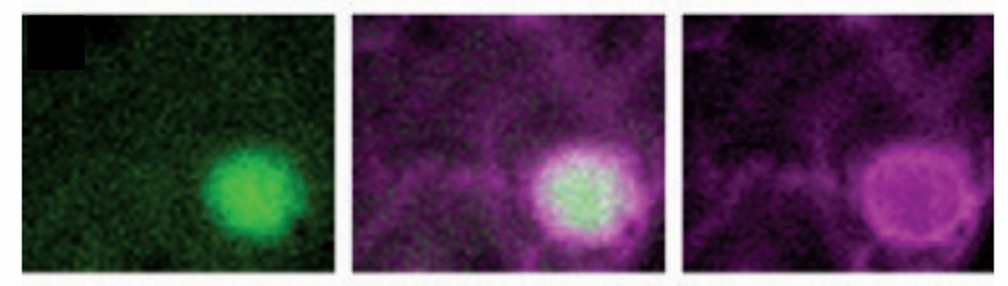 Fig.2 The bright YFP label is completely surrounded by the ER marker. (Nelson BK, et al., 2007)
Fig.2 The bright YFP label is completely surrounded by the ER marker. (Nelson BK, et al., 2007)
Lifeasible has a long-term commitment to the development and application of plant endoplasmic reticulum. We are pleased to use our extensive experience and advanced platform to provide satisfactory service and qualified products to meet the needs of our customers. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
References
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025