Resistance identification mainly identifies traits such as disease resistance, insect resistance, cold resistance, and drought resistance. Lifeasible is a leading global life sciences company that provides reliable solutions for plant drought resistance identification to evaluate the drought tolerance of plants to screen for resistant varieties.
Plants are subject to various biotic or abiotic stresses from the external environment during their growth and development, of which drought is one of the most important abiotic stresses. Moisture is an important environmental factor that determines the structure and function of ecosystems in arid and semi-arid ecosystems, and it is an essential component of plants and one of the necessary conditions for their survival. Both prolonged droughts and short-term water deficits may cause serious and irreversible injuries to plants, affecting their growth and development and crop yields. Plant drought tolerance refers to the ability of plants to not only survive but also maintain normal or near-normal metabolic levels and normal growth and development processes under drought conditions. Drought tolerance in plants can be categorized as drought avoidance, drought resistance, and drought tolerance.
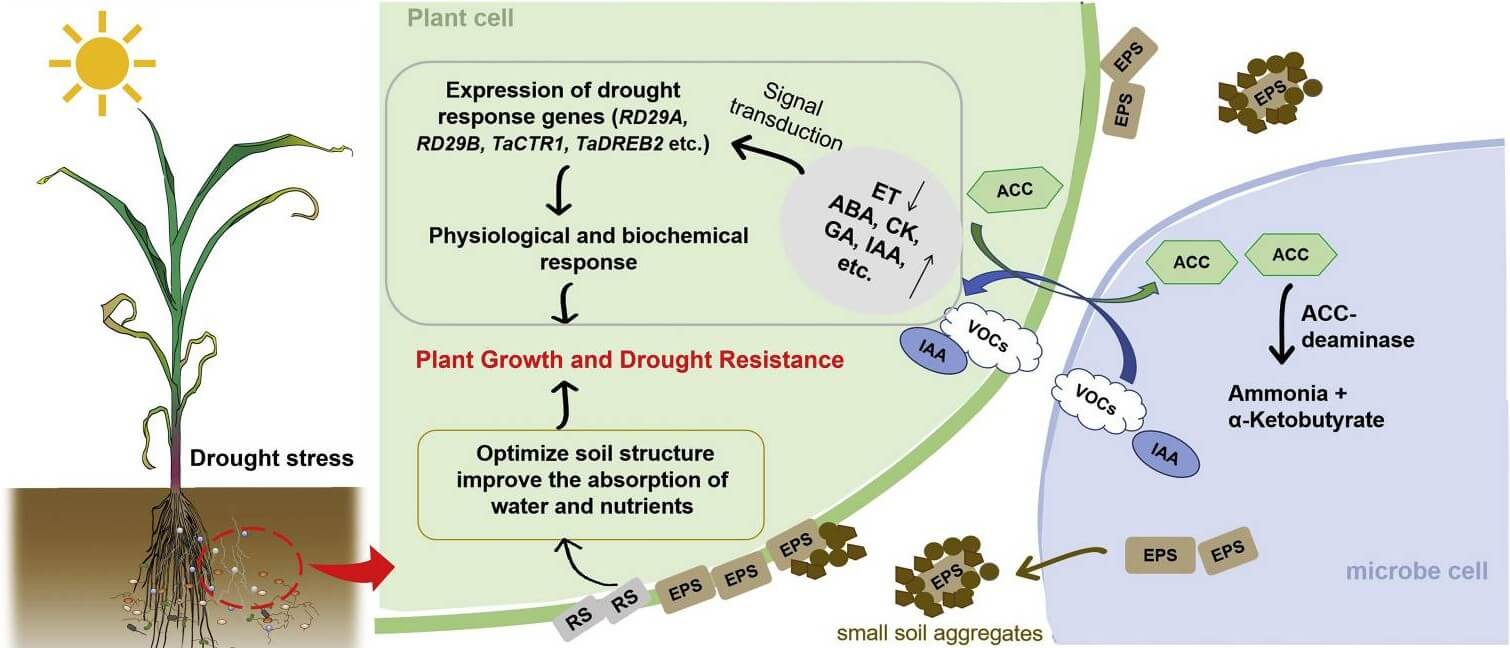 Fig. 1. Mechanistic pathway for PGPR-mediated drought tolerance in plants. (Zhang et al., 2022)
Fig. 1. Mechanistic pathway for PGPR-mediated drought tolerance in plants. (Zhang et al., 2022)
Lifeasible provides professional plant drought resistance identification solutions to customers with both direct and indirect identification methods. Depending on where the plant is growing or planted and how it has been treated, we will choose the best method for you.
We offer a variety of direct identification methods, including field identification, drought shelter or greenhouse methods, growth chamber or artificial climate chamber methods, potting drought methods, atmospheric drought methods, and hypertonic solution methods.
Field Identification
This method evaluates the drought resistance of plants by controlling irrigation water under natural conditions to create different degrees of drought stress. This method is simple and easy to implement, and the results obtained are relatively reliable under the local conditions of the experiment. Still, it is affected by environmental conditions and is difficult to repeat. This method is mostly used for the identification of drought resistance of crops.
Drought Shelter or Greenhouse Method
This method is to identify varieties planted in simulated climatic conditions that can be artificially controlled moisture by comparing the changes in drought indicators to evaluate the drought resistance of varieties. This method can overcome the non-repeatability of field identification and facilitate comparison, making the results more reliable. The disadvantage is that it requires certain equipment and energy consumption which cannot be carried out in large quantities, while the difference in environmental conditions between the drought shelter and the outside world may bring experimental errors.
Potting Drought Method
Potting identification mainly includes soil and sand cultivation through the control of soil moisture content of soil cultivation or sand cultivation plants and causes plant drought stress to identify the drought resistance of plants. This method is the most common drought treatment for plant drought resistance identification.
Atmospheric Drought Method
In this method, the plants to be identified are grown in an arid room where air humidity can be controlled. The plants are subjected to drought stress through dry air combined with the determination of some indexes to identify the strength of drought resistance, or chemical desiccants are sprayed on the foliage of the plants. The drought response of the plants is measured to identify the drought resistance of different strains.
Hypertonic Solution Method
This method uses sand culture or hydroponics to cultivate plants of a certain age and then transfer to different concentrations of PEG6000, mannitol, and other hypertonic solutions for drought treatment through the determination of some physiological and biochemical indicators to identify the drought resistance of different plants in the seedling stage.
Some drought resistance evaluation indexes, such as morphological and structural drought resistance indexes, physiological and biochemical drought resistance indexes, and growth and yield drought resistance indexes mainly carry out this method. In addition, we also provide molecular biology identification methods to establish RFLP genetic linkage maps by identifying quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for drought tolerance-related traits through restriction fragment length polypeptide RFLP marker probes or other molecular marker technologies. Specific RFLP marker probes can recognize the presence or absence of drought tolerance genes in the genetic material and thus identify the drought tolerance of the lines.
Lifeasible provides a variety of methods to identify and evaluate drought tolerance in plants, aiming to provide a reference for studying the molecular mechanism of drought tolerance in plants and molecular genetic breeding to improve drought tolerance in plants. If you are interested in our services, please contact us for the best solutions.
Reference
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025