Resistance identification mainly identifies traits such as disease resistance, insect resistance, cold resistance, and drought resistance. Lifeasible is a leading global life sciences company providing reliable solutions for identifying plant resistance to pests. Our goal is to help our customers make an accurate assessment of the ability of a crop variety, strain, or germplasm to resist a specific pest.
When plants of the same species are severely damaged by insects, some plants can avoid damage, tolerate damage, or have the ability to compensate despite damage. In agricultural practice, insect resistance indicates that a certain crop variety can achieve higher quality and higher yield than other varieties under the same pest population and environmental conditions. Plants that are less susceptible to insect damage or suffer less damage than other plants of the same species in the field are called insect-resistant plants. The insect resistance of plants is manifested in heredity. Although the degree of insect resistance is relative, breeding insect-resistant varieties of crops for certain pests so that they are not harmed or suffer less damage is an important part of integrated pest control. Crop insect resistance usually manifests itself in three ways:
(1) Insect repellent. Keep pests from eating it or laying eggs on it.
(2) Antibiosis. In the process of fighting pests, they have an advantage, causing the pests to grow poorly until they die.
(3) Insect resistance. Although it suffers from insect damage, it can compensate for its growth.
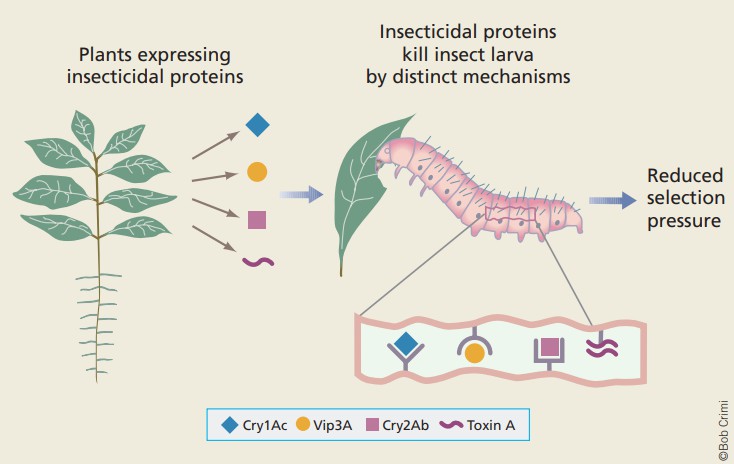 Fig. 1. Reducing the rate of insect resistance development. (Moar et al., 2003)
Fig. 1. Reducing the rate of insect resistance development. (Moar et al., 2003)
Pest resistance identification is the basic work of crop pest resistance breeding. Lifeasible provides professional plant pest resistance identification solutions to customers around the world. Our specific methods for identifying insect resistance vary from crop to crop and from insect to insect. We ensure that we provide you with a method that is both uncomplicated and faithfully reflects the degree of insect resistance.
We mainly conduct pest resistance identification at the seedling and adult stages of plants. The identification of aphid resistance is usually carried out at the seedling stage, and the identification of borer resistance is usually carried out at the adult stage of the crop. Insect resistance identification is ultimately based on crop yield.
We can identify the ability of plants to resist pests in natural and man-made environments.
We provide two methods: natural occurrence of pests and artificial infestation. The advantage of field identification is that it can directly reflect the comprehensive differences in insect resistance among crop varieties and identify highly resistant individual plants. The disadvantage is that it is susceptible to interference from climate and natural enemies of pests. Especially when evaluating yield, it is also affected by the uniformity of soil fertility and the different production performance of crop varieties. Therefore, we use field techniques, sampling methods, and statistical analysis techniques to make correct evaluations. In addition, it should be carried out at more points and repeated for at least one year.
This method is an indoor identification performed in greenhouses, laboratories, and growth chambers. Manual vaccination is required. Mainly used in preliminary screening of large amounts of germplasm resources. However, since the indoor man-made environment cannot fully reflect the natural environment in the field, the results obtained are only preliminary. When some of the materials are selected for use in the future, repeated identification in the field is still needed.
Lifeasible can identify plant pest resistance traits either in the field or indoors. We aim to help you select the ideal high-yielding, high-quality insect-resistant crop varieties and utilize plant resistance to control pests. If you are interested in our services, please contact us for the best solutions.
Reference
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025