Propagation and Purification of Nematode Populations
Plant nematode disease has a wide geographic distribution and hosts, which is extremely destructive. To effectively control the occurrence and damage of root-knot nematodes, the biological characteristics, pathogenicity, and various prevention and control methods of these nematodes have been extensively and deeply studied. Still, the culture and preservation of root-knot nematodes have been relatively few.
Lifeasible develops an advanced platform that provides services to customers worldwide. We customize featured services according to customer needs with decades of experience in plants. In addition, we deliver satisfactory and reliable results and reports on time to our customers worldwide.
Propagation of Nematodes Using Living Host Plants
- A large number of nematodes at the same growth stage are needed for the identification of nematode activity in the host and the screening of substances for in vitro nematode activity test. The age of nematodes isolated from naturally infected soil or roots of infected plants is inconsistent, so it is important to cultivate nematodes artificially.
-
Lifeasible provides propagation of nematodes using living host plants, such as potted tomatoes, potatoes, water cabbage, and so on. Put the roots with root knots into a glass bottle, place them in a 28°C incubator and moisturize. Wash the roots with a little water every 24 hours. The washed water is poured into the root of infected tomato varieties and cultured in the greenhouse for about 45 days.
Propagation of Nematodes Using Bacterial Species
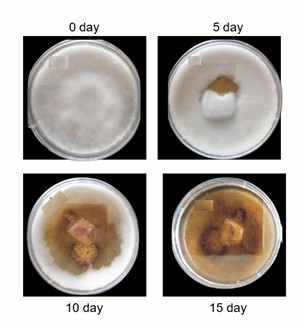 Fig.1 Growth of plant nematodes on medium.
Fig.1 Growth of plant nematodes on medium.
- To solve the problem that nematode culture depends on the host plant so that the whole life cycle of nematode can be completed in the petri dish, we also adopt a new method to culture nematode.
- We provide propagation of nematodes using bacterial species, such as Fusarium oxysporum f. spcubense, Fusarium solani, Botrytis cinerea, and so on.
| Steps |
Operation Methods |
| Separation of Nematode |
- The Behrman funnel method. The root is cut into small sections of about 1 cm. Sterile water is added to spread over the root tissue blocks. Nematodes swim out of the plant tissue when they encounter the water and at the same time, under gravity, sank to the connected tubules below the funnel to collect the root-knot nematodes in the tubules.
-
The oocysts and female adults of root-knot nematodes are searched for under an anatomic microscope and are picked out with an anatomic needle and placed in a petri dish.
|
| Preparation of Medium |
-
The mycelium is activated under the constant temperature of 28°C, and a small amount of mycelium is selected and cultured in PDA liquid medium after the mycelium is overgrown in the petri dish.
|
| In Vitro Culture of Nematodes |
- Inoculation of nematode. The density of nematode suspensions is about 50 / 100 μL after counting and dilution under the microscope. Then, the nematode suspension is inoculated onto the cultured medium.
- Nematode collection. A little sterile water is dropped from one side of the medium dish, and the sterile water is slowly waded down, and most nematodes are obtained by standing for 5 min.
-
Culture and preservation by sub-generation. The nematodes are washed from the original medium by the water flow method, and the nematode suspension is prepared again and then inoculated on the new medium for culture.
|
Lifeasible offers professional propagation and purification of nematodes to meet your research needs. With years of experience in plants, our advanced platforms can help our clients solve various difficulties and conduct research. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
For research or industrial raw materials, not for personal medical use!
 Fig.1 Growth of plant nematodes on medium.
Fig.1 Growth of plant nematodes on medium.