Sheep are crucial agricultural industry organisms that provide high-quality meat, fur, and milk. They are also widely used as laboratory animals in immunology, physiology, nutrition, microbiology, and other disciplines. Goats and ovine are gentle, non-aggressive, and well-adapted to various environments, making them suitable for surgical procedures, medical testing, and research on various disease models.
The sheep genome has been sequenced, and scientists can further explore the functional regions of the genome through ChIP-seq technology to study the genes that affect metabolism, growth and development, and appearance phenotype of sheep.
Lifeasible has long been engaged in epigenetic sequencing technology services and has built a complete animal laboratory base and sequencing platform, which can provide customers with sequencing services for many types of animals. Our sheep ChIP-seq service can quickly help clients analyze protein-DNA interactions, assess chromatin-associated protein modifications, and investigate possible regulatory mechanisms of target proteins.

Selective splicing in the genome may lead to changes in phenotype and biological function, and studies have identified CCCTC binding factors involved in regulating sheep meat tenderness. We used ChIP-seq to detect CCCTC binding factors, which not only allowed us to combine with genomic data to identify critical isoforms associated with meat tenderness but also revealed the biological mechanisms by which selective splicing regulates lamb tenderness.
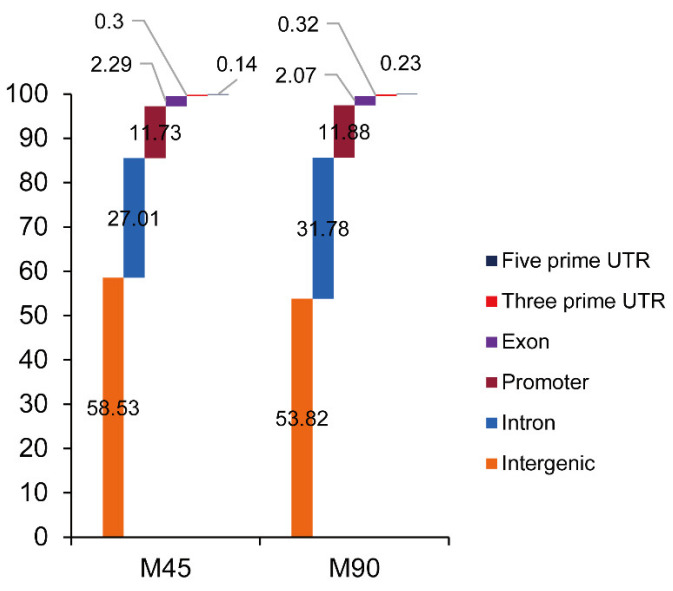 Figure 1. Read distribution of CTCF chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) among sheep genomes. (Yuan, Z, et al. 2022)
Figure 1. Read distribution of CTCF chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-seq) among sheep genomes. (Yuan, Z, et al. 2022)
Based on the available genome-wide data, we used ChIP-seq to identify the enrichment of histones bound to H3K4me1 and H3K27me3 genes and to analyze the mechanisms regulating growth and development, metabolism, immunity, and locomotion to reveal the regulatory regions of ovine genes.
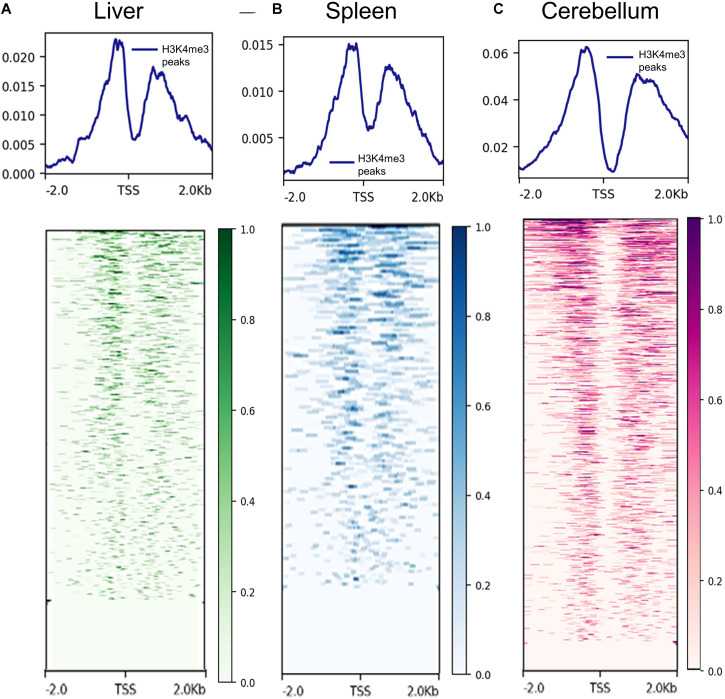 Figure 2. Data of H3K4me3 in different tissues detected by ChIP-seq. (Davenport, K. M, et al. 2021)
Figure 2. Data of H3K4me3 in different tissues detected by ChIP-seq. (Davenport, K. M, et al. 2021)
ChIP-Seq analysis of H3K4me3 and H3K27ac in sheep tissues was performed to assess the effect of human domestication on sheep regulatory sequences and to verify the role played by protein-coding genes and proximal regulatory elements in the evolution of sheep species.
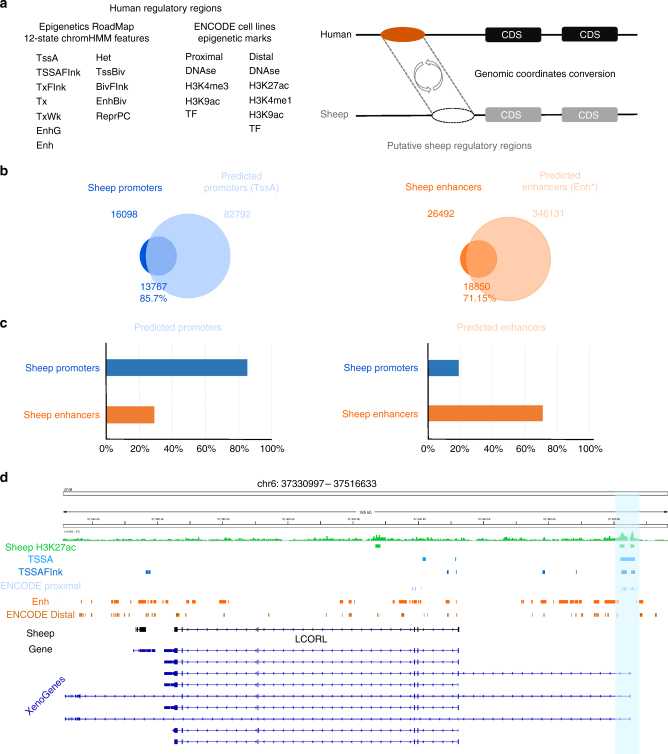 Figure 3, Preliminary functional annotation of the sheep genome by ChIP-seq detection and analysis. (Naval-Sanchez, M, et al. 2018)
Figure 3, Preliminary functional annotation of the sheep genome by ChIP-seq detection and analysis. (Naval-Sanchez, M, et al. 2018)
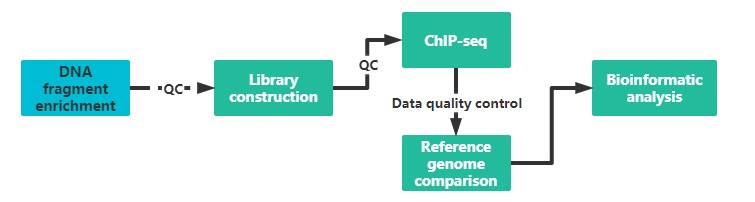
It is recommended to provide two sample preparations, if possible, to ensure the quality and continuity of the experiment.
As a world-renowned biotechnology services company, Lifeasible offers a wide range of sheep ChIP-seq technology solutions to help our customers quickly and accurately analyze functional genes, gene regulatory elements, and histone chromosome binding. If you would like to ask any questions, please do not hesitate to contact us.
References
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025