The plant endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a polymorphous network of interconnected membranes found throughout the cell cortex, sandwiched between the plasma membrane and the large tonoplast and contiguous with the nuclear envelope. The plant ER crosses the cell as a membrane bundle, forming trans-vacuolar chains by invagination of the vacuolar membrane, which is normally one or two per cell. At the cell cortex, the structure of the ER network consists of interconverting tubules and cisternae. Similar to other eukaryotes, the tubules and edges of the endoplasmic reticulum cisternae in plants have positive curvature.
Lifeasible, as a leading global company, is committed to helping our customers achieve effective and successful research. We provide observation, shaping, and analysis of protein location in plant endoplasmic reticulum. In addition, we deliver reliable results and reports on time to our customers worldwide.
Based on the ability of fluorescent dyes to visualize the ER network in living cells, Lifeasible provides fluorescent protein technology and advanced quantitative imaging technology to observe the structure of plant ER to help uncover the plant-specific mechanisms behind ER structure and dynamics.
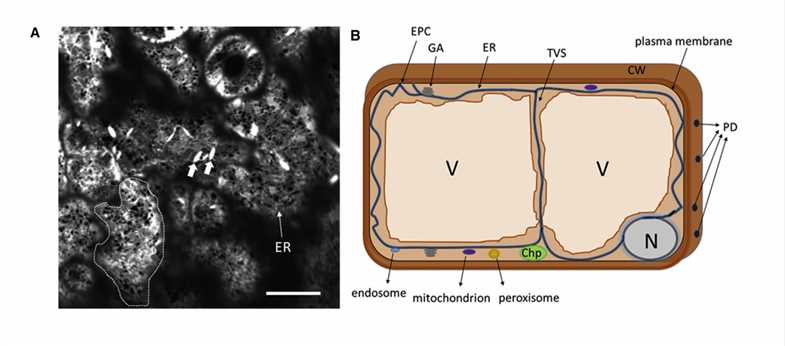 Fig.1 The plant ER network forms a reticular structure in the cell cortex. (Brandizzi F., 2021)
Fig.1 The plant ER network forms a reticular structure in the cell cortex. (Brandizzi F., 2021)
Lifeasible is always devoted to providing high-quality and satisfactory service to our customers. If you are interested in our services or have any questions, please feel free to contact us or make an online inquiry.
Reference
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025