Lifeasible provides TALEN-based gene-editing services to facilitate the application of gene editing technology in plant protection. We are skilled in TALEN-based plant gene editing.
TALEN-based gene editing technology is the first gene editing tool that is relatively easy to design and manufacture. TALEN is composed of a transcription activator-like effector (TALE) DNA binding domain and a FokI nuclease domain (Fig. 1). Repeat variable diresidue (RVD) at positions 12 and 13 of each repeat determines the specificity of TALE and TALEN. The flexibility and precise targeting of TALEN are unparalleled. The DNA binding specificity of TALEN can be altered at will by rearranging the repeats. TALEN-based gene editing can also be used for methylation-dependent gene manipulation. Those make TALEN-based gene editing technology promising for a wide range of applications. The technology has been used to edit various plants, including rice, wheat, maize, Arabidopsis, and tomato.
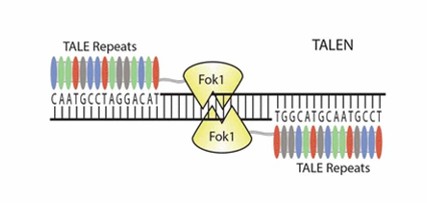 Fig. 1 A TALEN is composed of two monomers, with each containing a TALE DNA binding domain and a FokI nuclease domain (Malzahn et al., 2017).
Fig. 1 A TALEN is composed of two monomers, with each containing a TALE DNA binding domain and a FokI nuclease domain (Malzahn et al., 2017).
We take full advantage of the flexibility and strong targeting ability of TALEN-based gene editing for plant protection-related plant editing. The advantages of our services are as follows.
Upgraded targeting capabilities
We offer multiple ways to enhance the targeting ability of TALEN-based gene editing. In determining the TALEN target sites, we select sites containing more than three G or C deoxyribonucleotides that can interact with the "strong RVD". In addition, we avoid selecting target sites that contain multiple A or T deoxyribonucleotides at the beginning or end.
For the construction of TALEN, we follow the following high-targeting strategies.
Efficient construction of repeats and vectors
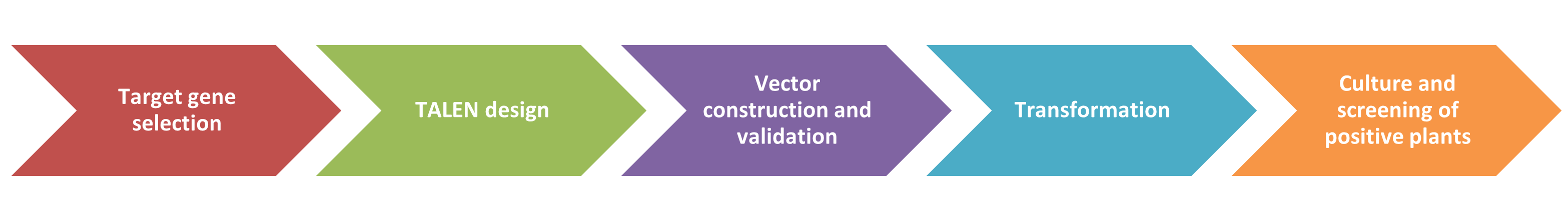
TALEN-based gene editing tools are much more challenging to construct than CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing systems. TALEN contains many repetitive sequences and has a large structure, which makes its construction difficult. We use two main methods to efficiently construct TALEN-based gene editing systems. Once the structure of TALEN has been determined, we can complete its construction within a single day.
(1) Golden Gate clone-based construction method
The Golden Gate cloning method can be a powerful method for the efficient construction of complex vectors that allow simultaneous enzymatic cleavage and linkage.
(2) Pre-assembled construction of domains and repetitive modules
We pre-assemble vectors containing the C- and N-terminal domain genes of TALE based on common plant types, and we pre-assemble hundreds of vectors containing 3-4 repeats. This greatly enhances the efficiency of TALEN construction.
Multiple delivery methods
We offer multiple ways to deliver TALEN-based gene editing systems, including Agrobacterium-mediated delivery, particle bombardment, nanomaterial delivery, microinjection, electroporation, and PEG delivery. We can also achieve DNA-free delivery of TALEN-based gene editing systems. Depending on the target plant and the customer's needs, we help to choose the appropriate delivery method.
TALEN-based gene editing technology offers greater flexibility than CRISPR/Cas9. Lifeasible provides professional TALEN-based plant gene editing services. Please do not hesitate to contact us!
References
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
January 27, 2025
Decomposition of Auxin by Plant Rhizosphere Microorganisms
January 25, 2025