Mycotoxins are secondary metabolites produced by certain fungi under specific conditions, which not only contaminate food and cause food poisoning in tea drinkers, but also some mycotoxins are carcinogenic, teratogenic, mutagenic, and other chronic toxic effects, posing a significant threat to health. There are over 400 fungal toxins, including aflatoxin B, aflatoxin M, aflatoxin G, fumonisins, ochratoxins, zearalenone, deoxynivalenol, T2 toxin, and orange penicillin, etc. Tea is recognized as one of the world's most popular beverages due to its richness in polyphenolic antioxidants, catechins, and minerals. However, tea can be contaminated with fungi in tropical climates and under harsh storage conditions or at various stages of drought, insects, and cultivation with medication and mechanical damage.
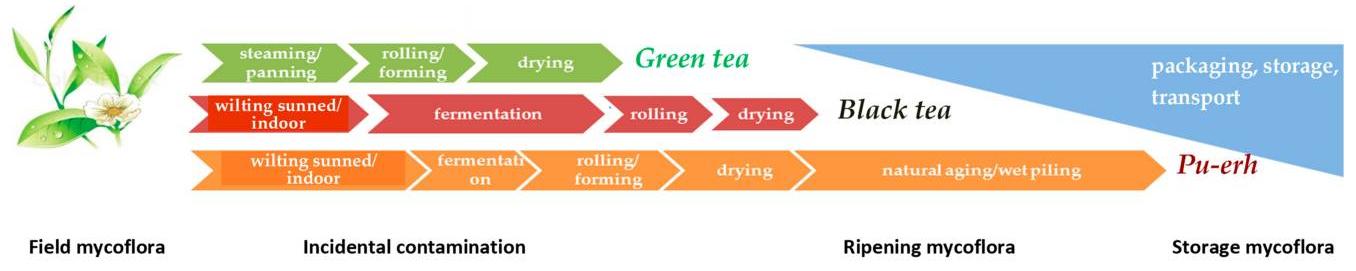 Fig.1. The common types of tea processing stages and associated mycoflora. (Sedova I, et al, 2018)
Fig.1. The common types of tea processing stages and associated mycoflora. (Sedova I, et al, 2018)
The EU Directive 98/53/EC has limits for various types of mycotoxins, but the types are limited to cereals, pulses, nuts, milk, and dairy products. Mycotoxins in tea are almost not regulated. However, the detection of mycotoxins in tea is becoming increasingly important. We have stronger and easier sample pre-treatment techniques and assays for detecting mycotoxins in food, tea, herbal medicine, and feed.
Fungal contamination of tea at any stage of commercial production can pose a serious health risk. As a recognized leader in tea testing, Lifeasible can help you develop the best solution for tea toxin detection based on sample matrix characteristics and the physicochemical properties of mycotoxins, primarily for the detection of various mycotoxins in tea. Our methods for testing mycotoxins in tea are based on international standards.
The matrix of tea samples is complex, with many interfering substances, which can contaminate the instrument and interfere with the results. Therefore, we provide the following pretreatment techniques to extract and clean up tea samples to improve the accuracy and precision of the assay.
We offer LC-MS/MS as the primary technique for determining mycotoxins in tea, which has been widely used to determine mycotoxins in cereals, nuts, milk powder, and other samples with high sensitivity and low detection limits. We can detect the following mycotoxins in tea.
| Tea Toxins Testing Items | Tea Toxins Testing Methods |
|---|---|
|
|
Lifeasible aims to combine liquid mass spectrometry with QuEChERS pre-processing technology to detect multiple mycotoxins in tea. This method is simple and time-saving. Our efficient customer-focused service will guarantee the quality of your results and save you time and money. If you are interested in our solutions, please contact us for technical consultation and quotation.
Reference
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
Adaptive Evolutionary Mechanism of Plants
February 28, 2025
Unraveling Cotton Development: Insights from Multi-Omics Studies
February 27, 2025