Lifeasible is dedicated to using gene editing technology to enhance plant resistance and provides zinc finger nuclease (ZFN) -based plant gene editing services for plant protection-related plant editing.
ZFN-based gene editing technology is an important tool discovered for precise gene editing. The ZFN-based gene editing system consists of a DNA recognition element based on the zinc finger (ZF) protein and a DNA cleavage domain of the FokI nucleic acid endonuclease (Fig. 1). Each ZF domain recognizes three nucleotides. A dimerized ZFN-based gene editing system consisting of 3-4 ZF domains can recognize 18-24 bp of nucleic acid sequence, which has excellent specificity and precision. For plant protection, its first application was to edit maize plant genes to make maize tolerant to herbicides. The technique has now been used for gene editing in various substances, including Arabidopsis, rice, apple, and fig.
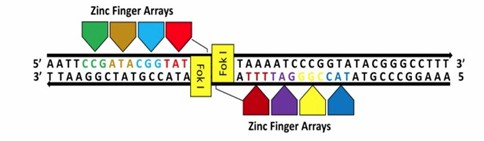 Fig. 1 Schematic representation of plant genome editing with Zinc Finger Nucleases (ZFNs) (Iqbal et al., 2020).
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of plant genome editing with Zinc Finger Nucleases (ZFNs) (Iqbal et al., 2020).
The advantages of ZFN-based gene editing systems are their excellent fidelity and small size. The construction of ZFN-based gene editing systems is very laborious. We offer services to help build highly specific ZFN-based gene editing systems to help achieve plant gene knockout, knock-in, and point mutation. Below are some of our building strategies.
The proven framework of ZF domains
We use the ZF domain framework that has been validated to have high DNA binding efficiency. Seven variable amino acid residues in the ZF domain framework are used to recognize the triplet bases. Between two nearby ZF domains, we use "T-G-E-K" sequences for ligation.
Screening for ZFNs with E. coli two-hybrid selection system
After determining the target, we will search for modular ZF proteins that can be used for gene editing according to the open platform developed by Zinc Finger Consortium and perform preliminary ZFN constructs. Then, we will screen for suitable ZFNs using the E. coli two-hybrid selection system.
Preserve proper spacing
ZFN-based gene editing needs to function as a dimer, and proper spacing between two ZFNs is required to perform better in generating double-strand breaks. We always reserve the optimal spacing space (5-6 bp) when designing ZFNs.
Mutant FokI to achieve higher specificity
The use of ZFN-based gene editing systems is mostly sought for their high fidelity. We offer the use of mutant FokI to achieve higher specificity in gene editing. The ZFN-based gene editing system based on mutant FokI cleaves DNA efficiently only when heterodimers are paired. In contrast, the efficiency of DNA cleavage is extremely low when heterodimers bound to DNA singly.
Different strategies for plant transformation
For different gene editing needs, we offer two main transformation strategies for ZFN-based gene editing, Agrobacterium-mediated transformation, and cell-penetrating peptide-mediated transformation. These two transformations are used to obtain ZFN-transformed and non-ZFN-transformed gene editing plants.
Lifeasible provides plant gene editing services related to plant protection. We can use high-fidelity ZFN-based gene editing technology to edit plant genes. We can also edit plants using CRISPR/Cas9 and TANEL-based gene editing techniques. Our services are professional and courteous. Please do not hesitate to contact us!
References
Lifeasible has established a one-stop service platform for plants. In addition to obtaining customized solutions for plant genetic engineering, customers can also conduct follow-up analysis and research on plants through our analysis platform. The analytical services we provide include but are not limited to the following:
Get Latest Lifeasible News and Updates Directly to Your Inbox
January 27, 2025
Decomposition of Auxin by Plant Rhizosphere Microorganisms
January 25, 2025