Gene editing has been one of the most important tools for researchers of life sciences, biochemistry, genetics and other biology-related fields. All organisms encoding and express genes in similar mechanisms, even they don't share similarity in genome size and gene numbers. Gene editing tools contribute a lot in understanding gene function, metabolic pathways, immune system, diseases and other vital activities.
Cyanobacteria is considered as the origin of chloroplast, due to their close relationship in phylogeny and high homology of their genomes. Thus, cyanobacteria are suitable model organisms for fundamental photosynthesis study. Besides, they can be genetically modified easily and be grown in simple medium.
With gene editing technology, genetically modified cyanobacteria strains can be used to study mechanisms of metabolism, including but not limited as follows.
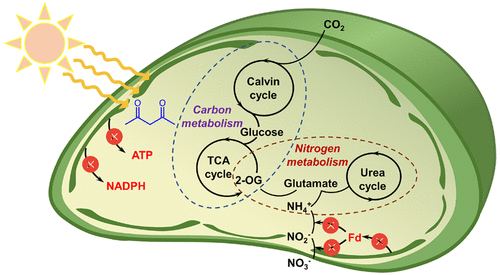 Carbon and Nitrogen Fixation in Cyanobacteria
Carbon and Nitrogen Fixation in Cyanobacteria
The model plant Arabidopsis thaliana has been studied thoroughly. The knockout collections of A. thaliana serve as an important resource in plant biology, which provide over 300,000 independent transgenic lines. With these collections, mutants of most gene are available. Except A. thaliana, there are many other model plants that have been studied thoroughly, including tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum), rice (Oryza sativa) and many other plants.
With gene editing technology, plants can be engineered to lose or gain traits, which indicate the function of genes in plants, as well as feasibility of exogenous gene expression in plants. Here are researches that can be studied with gene editing technology in plants.
| Plant Physiology | Plant Pathology |
|---|---|
|
|

Eukaryotic microbe like yeast serves as model organism of eukaryotes, which is widely used in genetics and cell biology. Due to the high homology between unicell yeast and other eukaryotic organisms and its simple structure, many proteins important in human biology were first found in yeast.
Yeast has been serving as a model organism to identify and study those basic vital activities and conserved signal pathways, including cellular growth, division, stress-response, trafficking and secretion, as well as diseases related to these biochemical pathways.
| Cell Biology |
|
| Metabolic Pathways |
|
| Human Disease |
|
| Mechanism of Aging |
|
With advanced and mature gene editing platform RecoNase™, Lifeasible offers services including gene knock-in and gene knock-out in cyanobacteria, chloroplast and yeast. Our experienced scientists have established efficient and high-precision gene editing toolkit, in which our customers can get satisfying results on time. Please feel free to contact us, get started with our professional services.