Gene editing technology provides researchers tools of deleting, inserting or replacing genes in genomes of organisms. Gene editing technology has been used in medical field widely, including medicine producing, animal disease models and gene therapy.
Recently, many biopharmaceutics have been produced with the platform based on microorganisms like yeast and cyanobacteria. Such as recombinant human insulin, HPV vaccine, recombinant hepatitis B vaccine and so on.
And gene editing has contributed to generating human disease models as well. Genetically modified mice are the most common model for human diseases. They are genetically modified as model of cancer, diabetes, heart disease, lung disease, obesity, aging and so on. As the simplest eukaryotic, yeast also serves as model organism of some human diseases that have cellular phenotype. Such as inherited nonpolyposis colon cancers and Werner's syndrome.
Many organisms, especially microorganisms, are genetically edited to producing medical compounds for purposes like healing disease, producing vaccine, producing drugs and other medical purposes. These compounds isolated from organisms are called biopharmaceutics. It has had profound impact on medical fields, including oncology, neurology, cardiology and others.
Production of biopharmaceutics with yeast doesn't require expensive infrastructure, and it has high yield that can meet demands fast. By inserting gene coding for useful pharmaceuticals into yeast, they can be able to produce proteins with medical applications. The most popular hosts to express recombinant proteins are S. cerevisiae and P. pastoris, due to their rapid growth in protein-free media and the ability to secrete the product extracellularly. Today, yeast provide half of the world's insulin supply.
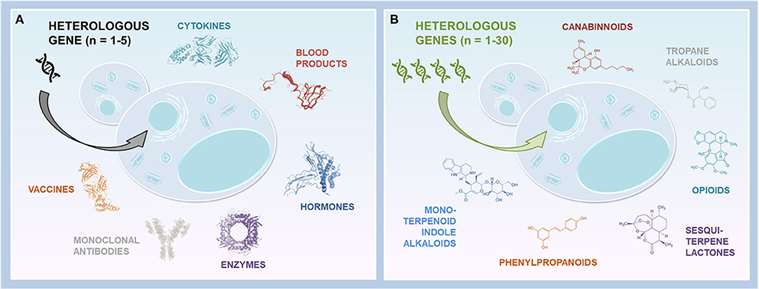 Yeasts as Biopharmaceutical Production Platforms (Natalja, et al. 2021)
Yeasts as Biopharmaceutical Production Platforms (Natalja, et al. 2021)
Due to the rapid development of gene editing technology, plants have been genetically modified to produce compounds with medical usage. Compared with animal, plants products don't carry animal pathogens that might be harmful for human beings. Additionally, engineering chloroplast genomes of plants has advantages like high-level expression and avoiding gene pollution spread with pollens.
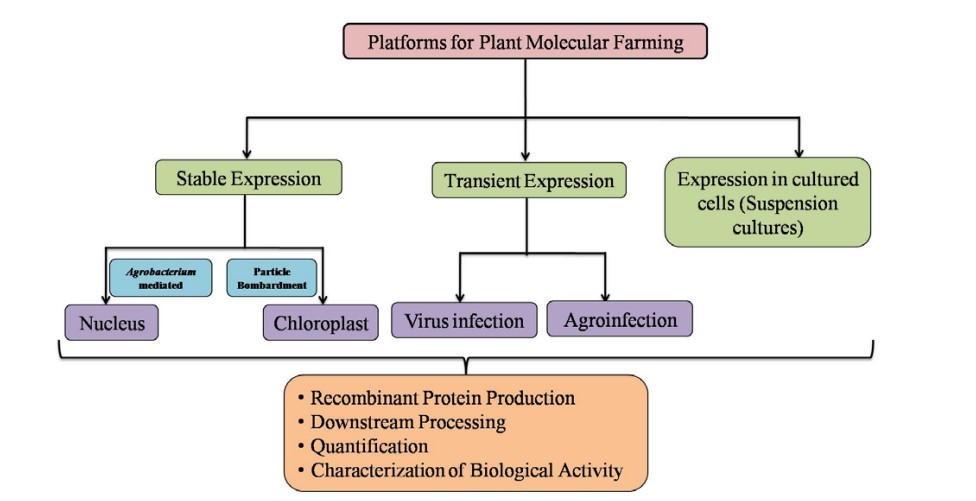 Strategy of Employing Plant to Produce Recombinant Pharmaceutical Proteins (Shanmugaraj, et al. 2022)
Strategy of Employing Plant to Produce Recombinant Pharmaceutical Proteins (Shanmugaraj, et al. 2022)
As photosynthetic microorganism, cyanobacteria can be grown under protein-free medium, which is cost-effective compared with other organisms. Besides, they have adaption to various conditions, including high concentration of its productions, which makes cyanobacteria a producer with high-titer. By inserting gene encoding proteins with pharmaceutical properties in cyanobacteria, bioactive compounds can be produced with high-efficiency and high-yield.
With advantages like high-efficient, high-yield and easily manipulated, yeast, cyanobacteria and plants have been employed to produce bioactive compound with pharmaceuticals properties. Here is list of some biopharmaceuticals produced with genetically modified organisms.
It's informative to study mechanisms of diseases on model organism without doing damage to human body. The most popular disease model are genetically modified mice, which has been induced artificially with many diseases, including cancer, diabetes, heart disease, lung disease, obesity, aging and so on.
Yeast genome has high homology with human genome, including many disease-related genes like proto-oncogenes. Genes cause hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer, neurofibromatosis type 1, ataxia telangiectasia and Werner's syndrome in humans have been found homology genes in yeast. They might accelerate the process of understanding the colon cancer and the aging caused by gene mutations in humans.
With advanced and mature gene editing platform RecoNase™, Lifeasible offers services including gene knock-in and gene knock-out in cyanobacteria, chloroplast and yeast. Our experienced scientists have established efficient and high-precision gene editing toolkit, in which our customers can get satisfying results on time. Please feel free to contact us, get started with our professional services.
References