Green manufacturing industry based on plants and microorganisms has been a popular topic in recent years. Organisms can be transformed with gene coding for a protein of value, such as industrial enzyme. Biotechnology in plants and microorganisms plays important role in biosynthetic processes especially in biofuels, secondary metabolites, bioenergy, waste treatment and bioremediation.

Biofuel can be produced from agriculture, industry and domestic waste. Compared with fossil fuel, biofuel can be produced in short time and it's considered to have negative emissions. The traditional technologies of producing biofuels are mainly utilizing base material that can be used as human supplement, such as corn, beet, wheat and other energy crops. However, due to the rapid development of biotechnology in recent years, genetically engineered organisms have been generated for synthetic applications.
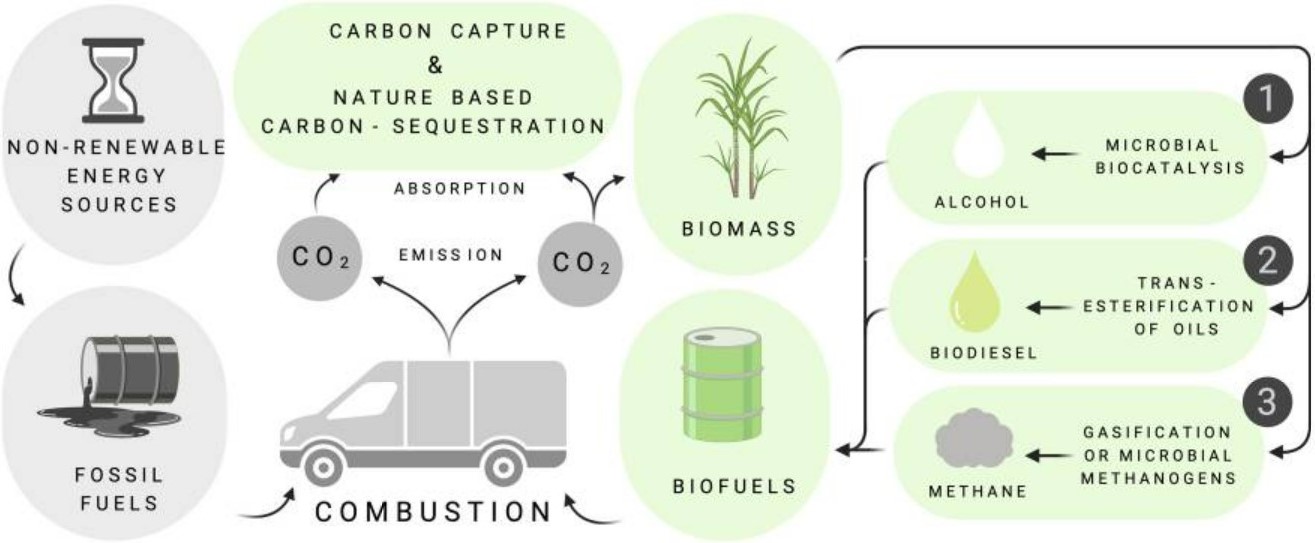 Routes to decarbonization by using biofuel (Love, et al. 2022)
Routes to decarbonization by using biofuel (Love, et al. 2022)
Cyanobacteria is potential candidate in sustainable industry, due to its ability of converting sunlight energy in to relatively stable chemical energy. As microorganism with simple structure and relatively small genome, cyanobacteria can be genetically engineered easily and they can also be grown in basal medium easily. They are genetically edited to produce compounds related to biofuels, such as ethanol, gasoline, butanol, methanol and fatty acid.
Algae is also emerging source for producing biofuel. The wastewater from domestic and industrial sources contain rich organic compounds can be used to grow algal cells. Besides, with gene editing technology, algal can be modified to have capacity to utilize other waste in different conditions, such as high salinity, extreme temperature, heavy metal and other stresses.
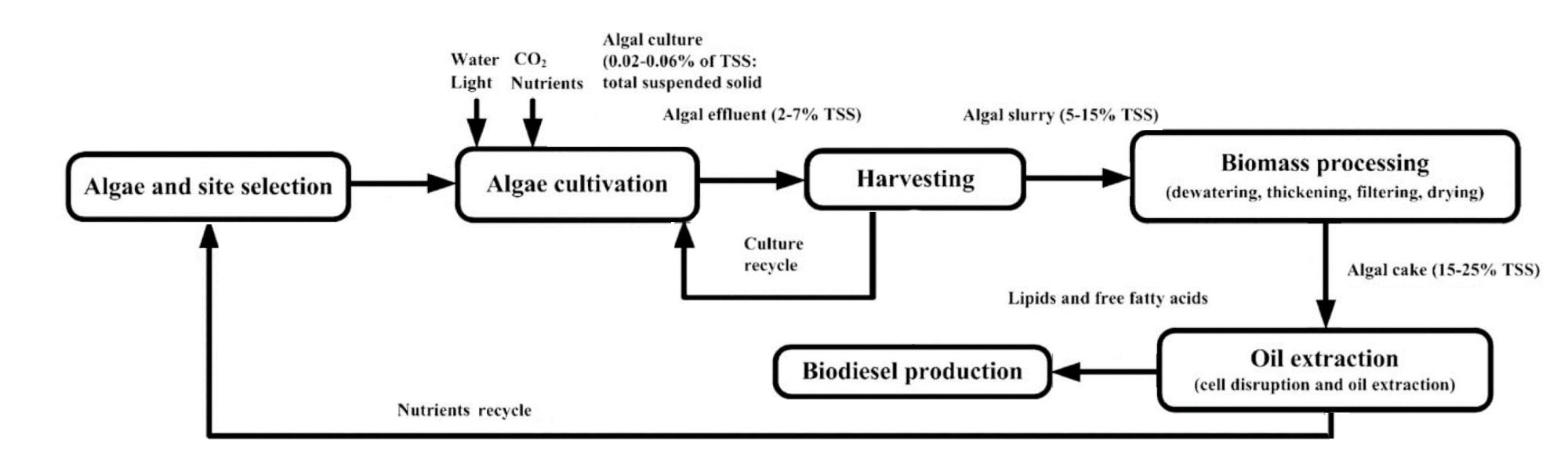 Stages of microalgae from cultivation to biofuel production. (Show, et al. 2017)
Stages of microalgae from cultivation to biofuel production. (Show, et al. 2017)
With advanced and mature gene editing platform RecoNase™, Lifeasible offers services including gene knock-in and gene knock-out in cyanobacteria, chloroplast and yeast. Our experienced scientists have established efficient and high-precision gene editing toolkit, in which our customers can get satisfying results on time. Please feel free to contact us, get started with our professional services.
References